Surface Chemistry of TiO2 and Co3O4 in Polypyrrole Nanocomposites: Influence on Congo Red Affinity and Adsorption Capacity
N. Baa, N. Belhouchat, M. Djama, I. K. Benramdane, I. Fadel, L. Bessah, A. Mudhoo, A. Sahli, Y. Larbah, L. Benhaddad
31 просмотров
Аннотация:
PPy and PPy-based composites were …
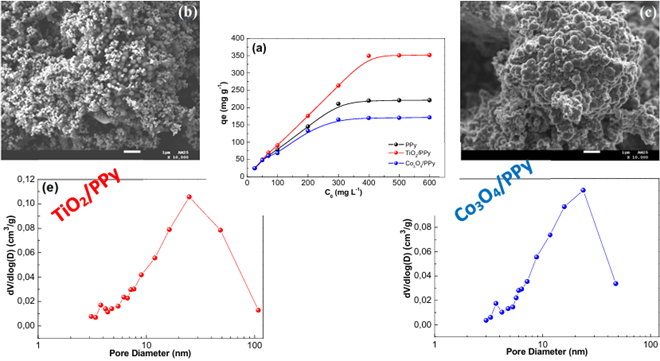
PPy and PPy-based composites were prepared. The composites were synthesized by adding TiO2 and Co3O4 metal oxides to PPy matrix. These three materials were tested for their ability to adsorb Congo Red (CR) dye. Their structure, morphology, and textural properties were analysed using XRD, FTIR, SEM–EDX and BET-BJH. The surface charge was measured using the point of zero charge (pHpzc). The results showed that the metal oxides were successfully incorporated to the polymer, which changed the surface morphology, pore structure, and surface charge characteristics. The effects of contact time, initial dye concentration, pH and temperature on adsorption were studied. PPy has the largest BET surface area (195.47 m2/g) as compared to TiO2/PPy (19.73 m2/g) and Co3O4/PPy (22.75 m2/g). TiO2/PPy sustained the highest CR adsorption capacity (351.75 mg/g), and this is due to synergistic effects nascent from the combined PPy functional groups and TiO2 surface chemistry. Co3O4/PPy exhibited the highest affinity for CR, attributable to the specific interaction between the Co2⁺/Co3⁺ sites and the anionic dye molecules. Kinetic results showed that the Shrinking Core Model (SCM) captured the experimental data best compared to pseudo-first order and pseudo-second kinetic models. The superior fit of the SCM suggests that a mixed mechanism controls diffusion through external film and intraparticle diffusion. Adsorption isotherm curve-fitting results showed that the Langmuir-Freundlich model provided the best fit for equilibrium data for CR adsorption, indicating both surface heterogeneity and non-uniform distribution of adsorption energies. Thermodynamic parameters revealed that the adsorption of CR is spontaneous and thermodynamically favourable.
Tannic-Acid-Functionalized TiO2 Nanoparticles for Adsorption of Rhodamine B and Crystal Violet from Aqueous Solutions
H. Yoo, P. D. Vu
36 просмотров
Аннотация:
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) …
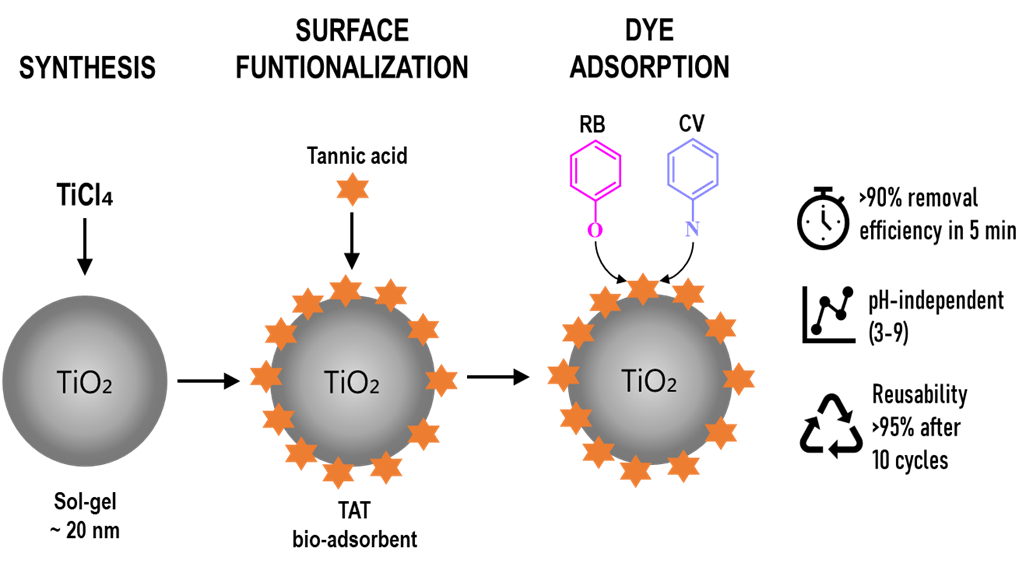
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) were synthesized via a controlled sol–gel method and subsequently functionalized with tannic acid (TA). The interaction of TA with TiO2 nanoparticles was evidenced by a visible color change and FT-IR analysis, consistent with surface complexation between phenolic groups and Ti4+ sites. The adsorption of cationic dyes, rhodamine B (RB) and crystal violet (CV), onto TA-functionalized TiO2 (TAT) was systematically investigated at room temperature by varying pH, initial dye concentration, contact time, and TAT dosage. Rapid dye uptake (>90% within 5 min) was observed for both dyes. Kinetic data were better described by the pseudo-second-order model than the pseudo-first-order model, reflecting adsorption controlled by surface site availability rather than a single diffusion step. Dye adsorption was largely pH-independent over the range of 3–9. Equilibrium data fitted the Langmuir model, suggesting monolayer adsorption with maximum capacities of 34.5 and 31.8 mg/g for RB and CV, respectively. TAT exhibited excellent reusability, retaining over 95% of its adsorption capacity after ten adsorption–desorption cycles using ethanol and inorganic acid. Overall, these results demonstrate that TAT is a stable, efficient, and regenerable bio-adsorbent for rapid removal of cationic dyes from water.