The study of chemical transformations on activated carbon with adsorbed vitamin C before and after thermal regeneration
Vasile Gutsanua, Maria Botnarua, Oleg Petuhov
Том 85 №3
330 просмотров;
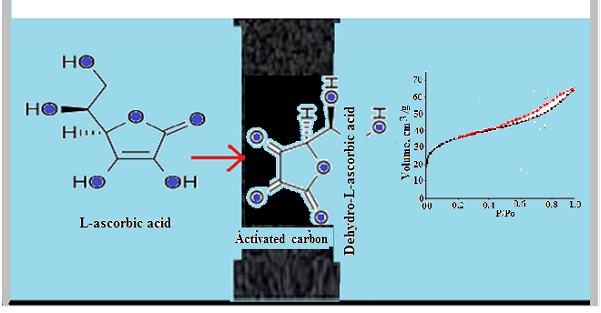
This article investigates the transformation processes of dehydro-L-ascorbic acid on commercial Granucol GE activated carbon when heat treated in air at a temperature of 350° C. It has been established that vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid) on coal is oxidized to dehydro-L-ascorbic acid before heating. It has been shown that dehydro-L-ascorbic acid decomposes with the formation of compounds with alcohol, carboxyl and carbonyl groups and the release of CO2 upon heating for 40 minutes. After regeneration, the sorption capacity of the coal decreases to 86.8%. During thermal regeneration, the state of the coal surface also changes. The data obtained from the isotherms of N2 adsorption show that the specific surface area and the pore volume of the regenerated coal are lower than those of the pure coal. dehydro-L-ascorbic acid molecules protect to some extent the active centers of the coal during heat treatment. A scheme of the processes of thermal degradation of dehydro-L-ascorbic acid on coal surface is proposed.