Investigation of Newly Developed 5-Aminoisophthalate Capped Gold Nanoparticles for Degradation of Azo-Dyes
Shamim Ahmed Khan and Tarun Kumar Misra
Том 85 №4
325 просмотров;
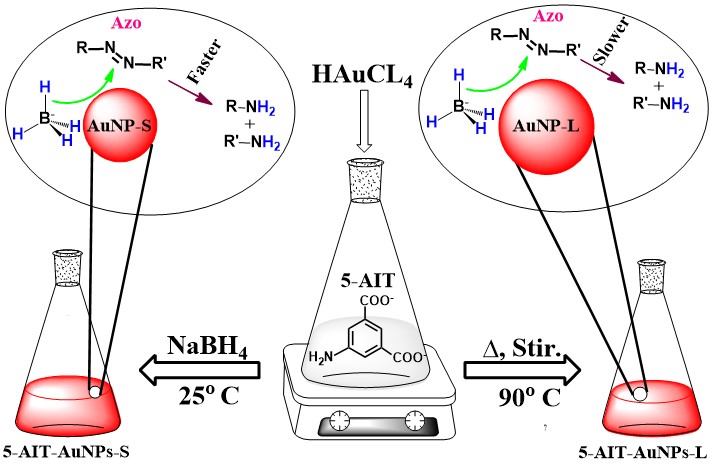
The sodium salt of 5-aminoisothalate (5-AIT), which has -NH2 and -COO-Na+ functions, is a highly water-soluble compound. It was used as reducing and capping agents to develop AuNPs. When sodium borohydride (SBH) was not used as a reducing agent, the developed methodology resulted in particles that were larger in size (5-AIT-AuNPs-L, 14±1.83 nm) than those obtained by the SBH-reduction method (5-AIT-AuNPs-S, 10±2.03 nm). The surface Plasmon resonance band for the smaller particles is centered at 520 nm, but it is positioned at 528 nm for the bigger particles. The particles have a wide window of pH tolerable range, i.e., pH 3 – 10. The capping agents adsorb onto the surface of particles, as evidenced by emission and the Raman spectroscopies and computation analysis. The binding energy increases with the increase of cluster atoms and it is -1.85 eV for 5-AIT-Au5 cluster. The efficacy of the particles as dye-degradation nanocatalysts for not only well-reputed dye, methyl orange (MO) but also synthetic promising dyes (Uazo-1 and Uazo-2) based on 6-aminouracil was assessed. The degradation kinetics follow pseudo-first-order reactions. According to the findings, the smaller particles degrade the dyes more rapidly than the larger particles.