An experimental Study of a Magnetic Liquid Marble and a Novel Scheme for Improving the Sensitivity of a Liquid Marble-Based Accelerometer
E. Poorreza, R. HadjiaghaieVafaie, M. Mehdipoor, H. Badri Ghavifekr
Том 85 №4
303 просмотров;
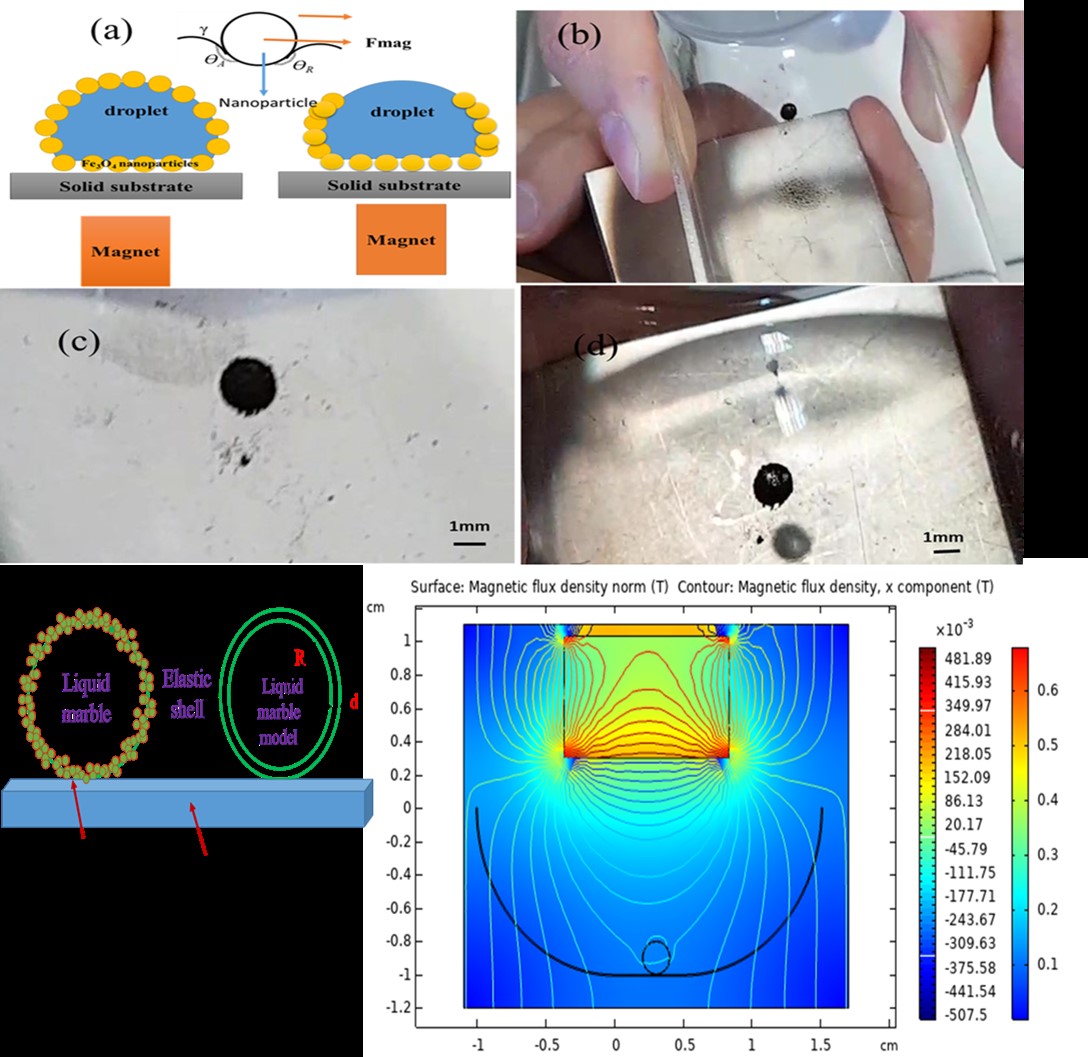
Due to the interfacial energy minimization phenomenon, rolling a liquid droplet on a solid powder bed consisting of hydrophobic micro-nano sized particles results in particle adhesion onto the droplet surface. These interesting flexible formations (known as dry waters or liquid marble) have attracted a great deal of attention in surface science. After the formation of a magnetic liquid marble with a radius of about 1.1 mm, reversible opening and closing of magnetic nanoparticle shell by the permanent magnet is conducted in the experimental part of this study. In the simulation part of our investigation, which is the novelty of our work, by modeling a liquid marble by a droplet with an elastic shell, the effect of gravitational force on the marble and its motion on a curved substrate were simulated by the Finite Element Method. A novel scheme for increasing the sensitivity of a liquid marble-based accelerometer is presented. The presented scheme for this investigation consists of a liquid marble placed on a curved surface which is manipulated magnetically by placing a permanent magnet above the curved surface. The produced magnetic force deforms the marble shape by opposing its weight, therefore causes the marble to get approximately spherical rather than puddle shaped form.