Single Silver Nanoparticles: Local Refractive Index Response to Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance and Molar Attenuation Coefficient
Mazen Alrahili
Том 86 №1
1080 просмотров;
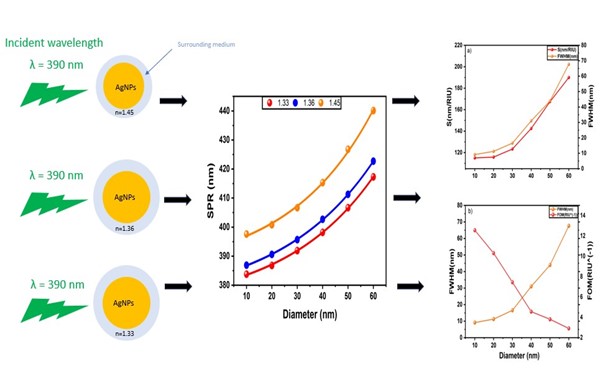
In this paper, we analyze the optical properties and sensitivities of spherical silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) with varying diameters (10–60 nm) in different surrounding medium, including water, ethanol, and chloroform. The investigation focuses on analytically assessing scattering efficiencies (Qsca ), absorption efficiencies (Qabs ), total extinction efficiencies (Qext ), shedding light on how the properties of AgNPs change with the size and surrounding medium of AgNPs. The results show that smaller AgNPs exhibit sharper plasmon resonance peaks at shorter wavelengths, while larger AgNPs display broader peaks in the visible spectrum, showcasing the size-dependent behavior of AgNPs. Additionally, the study calculates the molar attenuation coefficient (ε) and extinction cross section (σext ) for AgNPs, highlighting the differences in absorption properties between small and large particles and their sensitivity to the surrounding medium. The research also discusses the implications of these properties for applications such as plasmonic sensing and sensor design, emphasizing the importance of particle size and surrounding medium in optimizing sensor performance. Moreover, the refractive index sensitivity (S) and the figure of merit (FOM) are introduced as critical parameters for assessing sensor performance, revealing their relationship with particle size, and providing valuable insights into sensor design and optimization.