Novel Synthesis of ZnO-Ag2O Nanocomposite Crystals and their Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Activity Evaluation
Haoyu Li, Ruojun Ye, and Xingping Zhou
Том 86 №3
420 просмотров;
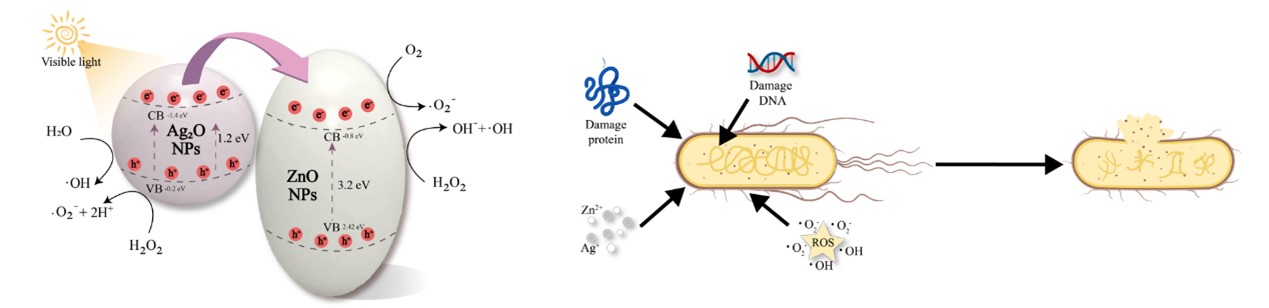
This paper reports on the successful preparation of a series of ZnO-Ag2O nanocomposite crystals with varying elemental contents by a novel oil-water interface method. The structures, compositions, microscopic morphologies, and optical properties of these crystals were characterized using HRTEM, SEM, XRD, EDX, XPS, UV-Vis, and PL measurements. The obtained well-dispersed hetero-structure nanocomposite crystals, with a particle size mainly ranged from 50 to 100 nm and a high purity, displayed a good absorption ability in the visible region. Virtually, the nanocomposite crystals exhibited a significant red-shift 5-15 nm in the UV diffuse absorption edge towards the visible range, accompanied by a substantial reduction in fluorescence absorption intensity. Importantly, the photocatalytic degradation of these nanocomposites was tested against Congo red (CR) dye under visible light excitation. The results revealed that the degradation efficiencies of ZnO-Ag2O nanocomposite crystals against CR under visible light were 9.4 and 2.7 times as high as those of pure ZnO and Ag2O nanoparticles, respectively. Also, the antimicrobial function of ZnO-Ag2O nanocomposite crystals was tested against harmful bacteria. The study results indicated that the diameters of inhibition zone of the nanocomposite crystals were respectively 13.5 mm for gram-negative Escherichia coli and 12.9 mm for gram-positive Bacillus subtilis, significantly larger than that of pure ZnO due to the synergistic effects of ZnO and Ag2O nanoparticles. The high photocatalytic efficiency and strong antimicrobial activity of ZnO-Ag2O nanocomposite crystals suggest their great significance in degrading pollutants and killing harmful bacteria.