INVESTIGATION OF MICRO-STRUCTURAL, OPTICAL AND THERMAL PROPERTIES OF SYNTHESIZED Zr DOPED SnO2 NANOPARTICLES FOR OPTOELECTRONIC APPLICATIONS
Nadeem Firoz, Jitendra Bahadur, Azra Parveen, Shraddha Agrawal, Shakeel Khan
Том 86 №6
427 просмотров;
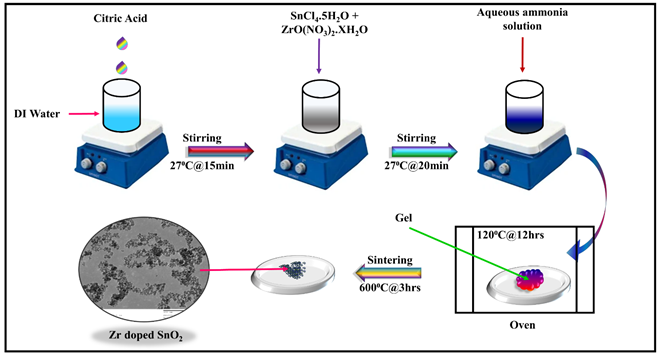
Pristine Tin Oxide (SnO2) and Zirconium doped Tin Oxide (SnO2:Zr) with varying composition Sn1–xZrxO2 (x = 3%, 5%, 7% and 10%) are synthesized using Sol-Gel method. The structural, optical, and thermal properties of synthesized pristine SnO2 and SnO2:Zr nanoparticles were examined by using various characterization techniques including XRD, SEM, TEM, FTIR, UV-visible, and TGA/DSC. The EDAX analysis confirmed the presence of Zr atoms within SnO2 phase. FTIR analysis revealed presence of various functional groups such as antisymmetric Sn-O-Sn stretching mode, symmetric Sn-O-Sn, Zr-O bonds, C-O stretching mode, and stretching vibration. TEM analysis indicated uniformity in polycrystalline grains within Zr doped SnO2 sample. UV-visible analysis demonstrated decrement in optical band gap which confirmed that Zr doping tuned the optoelectronic properties of SnO2 nanoparticles. Results combined with TGA/DSC analysis establish that 7% doping is the optimum limit after which steric hindrance effects destabilize the structural and thermal properties of the material. Therefore, Zr doping plays crucial role in modifying structural, thermal and optoelectronic properties of SnO2 thereby proposing their use in optoelectronic devices