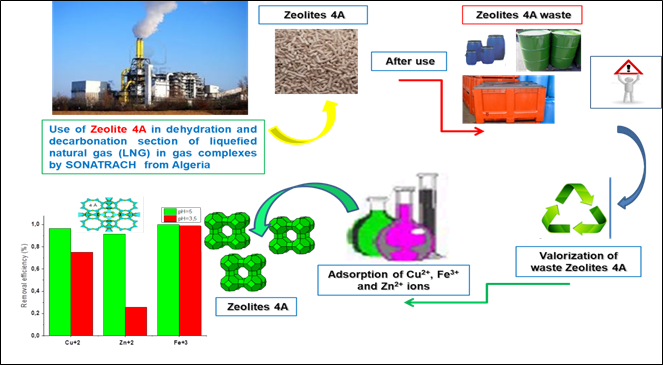
Adsorption of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Fe3+ Ions in a Ternary System from Aqueous Solutions on Industrial Waste 4A Zeolite: Characterization, Dynamic, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies
S. Bensafi, S. Amokrane, D. Nibou
Том 87 №1
284 просмотров;
The adsorption of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Fe3+ ions in a ternary system on waste zeolite 4A was examined under various experimental conditions (concentration, pH, Solid liquid ratio and temperature).The physicochemical and micro structural characterization (X-ray Diffraction, Scanning Electron Microscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, X-ray Fluorescence, Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy and Thermogravimetry/Differential Thermal Analysis) techniques were applied. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy was highlighted the bands characteristic of functional groups Me-(H2O), O-H (H2O), C-O, Me-Si-OH, Me-O and Si-OH of 4A and adsorbed by Cu2+, Fe3+ and Zn2+ ions (CFZ4A). The nature and coordination environment of these species were demonstrated by Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy. The results show that the experimental adsorption capacities of the studied ions in the ternary system were respectively 79.125, 47.207 and 95.185 mg/g for Cu2+, Zn2+ and Fe3+. Temkin, Dubinin-Radushkevich and Freundlich equilibrium models give the best fit for the Cu2+, Zn2+ and Fe3+ ions according to R2 and the minimum values of Akaike information criteria. Elovich and Double exponential kinetics models are most appropriate to describe the adsorption data of Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions and Johnson-Mehl-Avrami model describes well the Fe3+ ions. The increase in temperature leads to a decrease in the free energy which indicates that the reaction is spontaneous and more favorable at high temperatures. The fixation of copper, zinc and iron ions in a ternary system on the waste of commercial zeolite 4A shows certain selectivity according to the following order: Fe3+> Cu2+>Zn2+.