Microwave Assisted Au Nanoparticles Production Using Waste Avocado Seed Extract: Characterization, Antioxidant, and Antibacterial Activities
K. Ramesh, G. Bhagavanth Reddy, Venkatramulu Gopi, M. Noorjahan
Том 87 №3
211 просмотров;
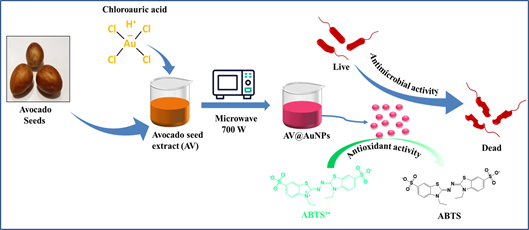
This study presents a rapid and eco-friendly approach to synthesize gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) using waste avocado seed extract (AV) as a reducing and capping agent. Microwave irradiation enables the synthesis of AuNPs within a minute, as evidenced by the solution's characteristic red color and confirmed by a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peak at ~530 nm in the UV-visible spectrum. Synthesis parameters, including pH and concentrations of AV and gold chloride, were optimized, revealing that mild alkaline conditions favor AuNP formation, while acidic conditions are detrimental. The AuNPs, characterized by TEM, exhibited a small size (9.9 ± 3.6 nm) and spherical morphology without aggregation. X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed the face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure of the AuNPs, and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy indicated the involvement of functional groups in AV in the reduction and stabilization of the nanoparticles. The AV@AuNPs demonstrated excellent stability, as indicated by a high negative zeta potential (-27.0 ± 6.4 mV). Additionally, the nanoparticles showed strong antioxidant activity comparable to ascorbic acid and significant antibacterial efficacy against both Gram-positive (S. aureus and B. subtilis) and Gram-negative (E. coli and P. aeruginosa) bacteria, with a pronounced effect on Gram-negative strains.