Analytical Comparison of Geometric and Harmonic Mean Forms of Solid/Liquid Interfacial Tension Expressions
Yukihiro Kusano, Reinosuke Kusano
Том 88 №3
24 просмотров;
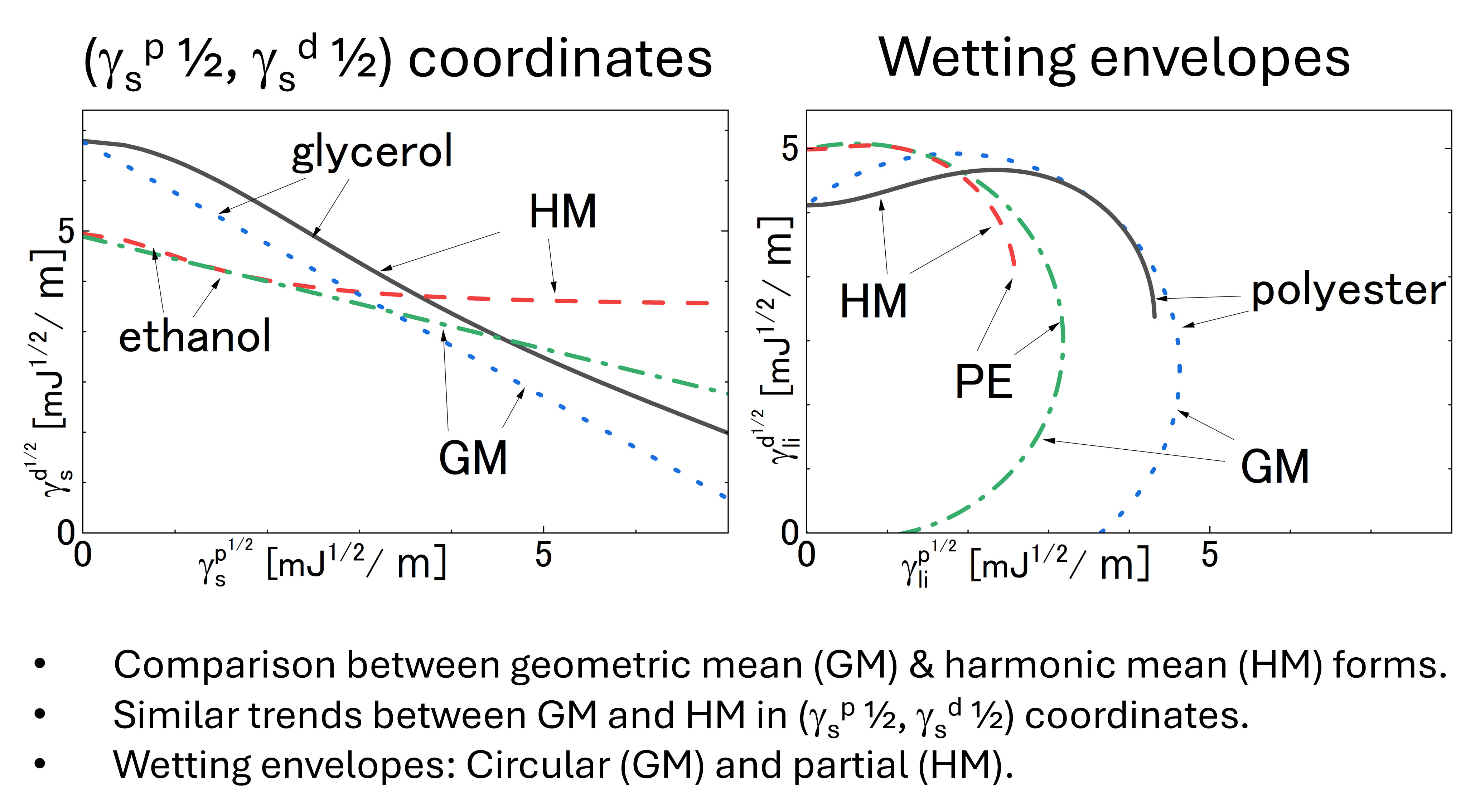
The surface tension of a liquid or solid is often expressed by two components, namely dispersion and polar components. The geometric mean form is generally used to formulate interfacial tension of two dissimilar materials. However, there have been claims that the harmonic mean form is more accurate than the geometric mean form. In the present work, theoretical backgrounds of the geometric and harmonic forms are briefly reviewed, and differences between these forms are analytically compared. When solid surface tension is calculated using known liquid surface tension and measured contact angles, the values obtained by the harmonic mean form tend to be larger than those of the geometric form. The wetting envelopes may be formed only partially with the harmonic mean form, which may limit its practical use. The arguments to support the harmonic mean form are questionable, but it does not mean that the geometric mean form is more useful. Furthermore, it is noted that the choice of the database of given surface tension values affects the result when the geometric and harmonic forms are compared.