Clay-microalgae Biocomposite for Enhanced Nitrate Removal from Water
M. Tabatabaei Khodadadei, H. Mansouri, H. Salari
Том 88 №4
110 просмотров;
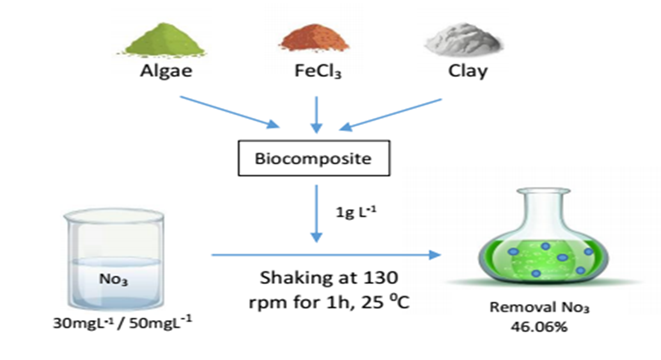
Live and dead microalgae have the potential to remove mineral nutrients such as nitrogen from water resources. In this research, the efficiency of biocomposites prepared from different ratios of dried biomass of Chlorella sorokiniana microalgae together with kaolin and iron chloride for nitrate removal from water was investigated. The effect of pH on the nitrate adsorption capacity of microalgal biomass for different initial nitrate concentrations (30 and 50 mg L-1) was studied. The optimum pH value was found to be about 5. The adsorption efficiency decreased at higher pH. The best performance was achieved by the 50% algae + 50% clay biocomposite, with an adsorption capacity of 14.25 mg g-1 (47.5%) of nitrate at a concentration of 30 mg L-1. The biocomposite of 50% algae + 35% clay + 15% FeCl3 also showed similar performance in nitrate adsorption at a concentration of 30 mg L-1 (46.06%). With increasing nitrate concentration, the removal by microalgal biomass and biocomposites did not increase. Adding FeCl3 to the biocomposite did not increase nitrate adsorption compared to the 50% algae + 50% clay biocomposite. The lowest removal rate of 2.46 mg g-1 related to dry biomass was obtained at a concentration of 50 mg L-1. The morphological structure of the adsorbent was investigated by SEM microscopy and the functional groups by FTIR method. Based on the obtained results, it can be concluded that the prepared composite has a high ability to remove nitrate from water sources.