Tannic-Acid-Functionalized TiO2 Nanoparticles for Adsorption of Rhodamine B and Crystal Violet from Aqueous Solutions
H. Yoo, P. D. Vu
Том 88 №5
29 просмотров;
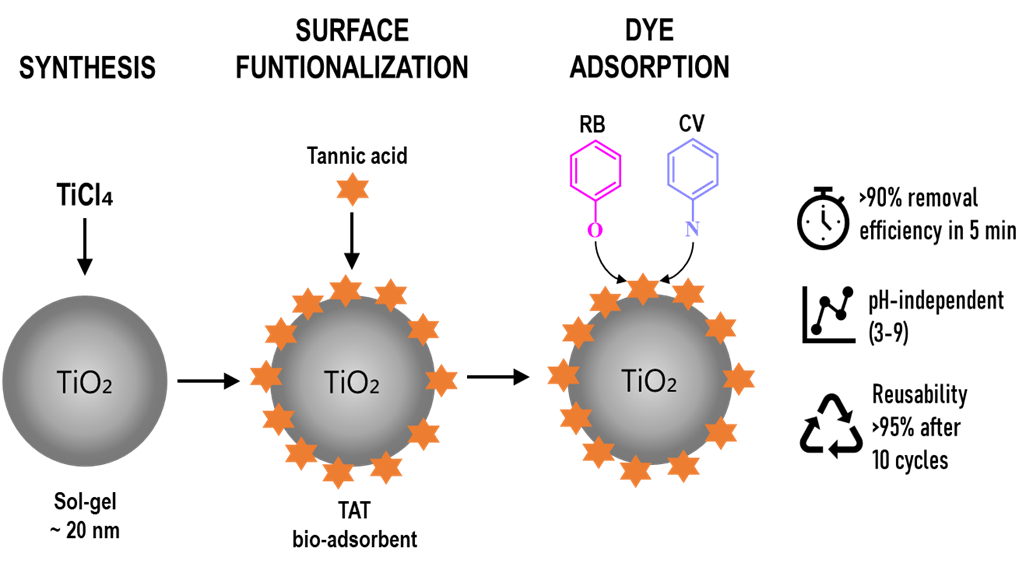
Titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO2 NPs) were synthesized via a controlled sol–gel method and subsequently functionalized with tannic acid (TA). The interaction of TA with TiO2 nanoparticles was evidenced by a visible color change and FT-IR analysis, consistent with surface complexation between phenolic groups and Ti4+ sites. The adsorption of cationic dyes, rhodamine B (RB) and crystal violet (CV), onto TA-functionalized TiO2 (TAT) was systematically investigated at room temperature by varying pH, initial dye concentration, contact time, and TAT dosage. Rapid dye uptake (>90% within 5 min) was observed for both dyes. Kinetic data were better described by the pseudo-second-order model than the pseudo-first-order model, reflecting adsorption controlled by surface site availability rather than a single diffusion step. Dye adsorption was largely pH-independent over the range of 3–9. Equilibrium data fitted the Langmuir model, suggesting monolayer adsorption with maximum capacities of 34.5 and 31.8 mg/g for RB and CV, respectively. TAT exhibited excellent reusability, retaining over 95% of its adsorption capacity after ten adsorption–desorption cycles using ethanol and inorganic acid. Overall, these results demonstrate that TAT is a stable, efficient, and regenerable bio-adsorbent for rapid removal of cationic dyes from water.