Surface Chemistry of TiO2 and Co3O4 in Polypyrrole Nanocomposites: Influence on Congo Red Affinity and Adsorption Capacity
N. Baa, N. Belhouchat, M. Djama, I. K. Benramdane, I. Fadel, L. Bessah, A. Mudhoo, A. Sahli, Y. Larbah, L. Benhaddad
Том 88 №5
32 просмотров;
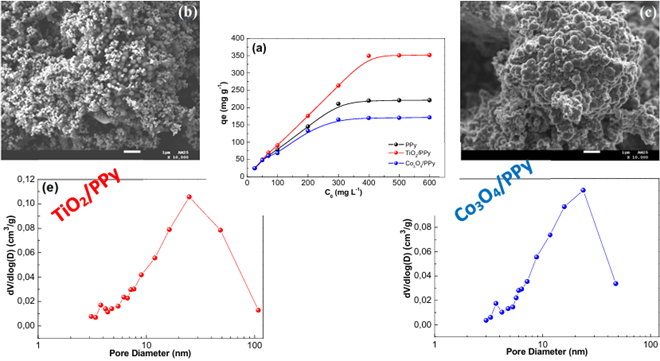
PPy and PPy-based composites were prepared. The composites were synthesized by adding TiO2 and Co3O4 metal oxides to PPy matrix. These three materials were tested for their ability to adsorb Congo Red (CR) dye. Their structure, morphology, and textural properties were analysed using XRD, FTIR, SEM–EDX and BET-BJH. The surface charge was measured using the point of zero charge (pHpzc). The results showed that the metal oxides were successfully incorporated to the polymer, which changed the surface morphology, pore structure, and surface charge characteristics. The effects of contact time, initial dye concentration, pH and temperature on adsorption were studied. PPy has the largest BET surface area (195.47 m2/g) as compared to TiO2/PPy (19.73 m2/g) and Co3O4/PPy (22.75 m2/g). TiO2/PPy sustained the highest CR adsorption capacity (351.75 mg/g), and this is due to synergistic effects nascent from the combined PPy functional groups and TiO2 surface chemistry. Co3O4/PPy exhibited the highest affinity for CR, attributable to the specific interaction between the Co2⁺/Co3⁺ sites and the anionic dye molecules. Kinetic results showed that the Shrinking Core Model (SCM) captured the experimental data best compared to pseudo-first order and pseudo-second kinetic models. The superior fit of the SCM suggests that a mixed mechanism controls diffusion through external film and intraparticle diffusion. Adsorption isotherm curve-fitting results showed that the Langmuir-Freundlich model provided the best fit for equilibrium data for CR adsorption, indicating both surface heterogeneity and non-uniform distribution of adsorption energies. Thermodynamic parameters revealed that the adsorption of CR is spontaneous and thermodynamically favourable.