The Cumulative Impact of DTAB Micelles and Ru(III) on the Rate Augmentation of 4-Chlorobenzaldehyde by N-Bromosuccinimide
A. Srivastava, P.K. Pandey, N. Srivastava, R. K. Padhy, N. Srivastava
Том 87 №5
177 просмотров;
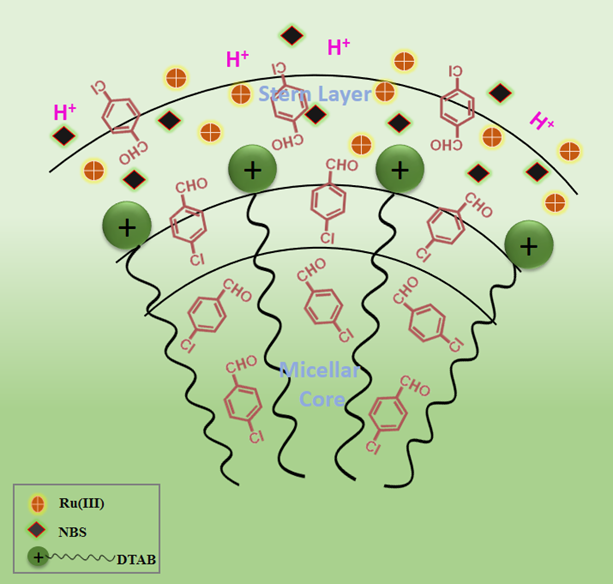
4-Chlorobenzoic acid (4-CBA) serves as an important industrial compound, utilized as a probe for hydroxyl radicals in ozonation processes, as well as a ligand in the synthesis of luminescent lanthanide complexes. 4-CBA can be produced from 4-Chlorobenzaldehyde (4-CBZ) via oxidation using a specific oxidizing agent. The oxidation kinetics of 4-CBZ by N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS), facilitated by Ru(III), have been investigated in both the aqueous and dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide (DTAB) micellar medium. The reaction's progression was assessed by quantifying unreacted NBS iodometrically. Throughout the range of concentrations analyzed, the 4-CBZ oxidation demonstrates a fractional-order kinetics concerning both [4-CBZ] and [Ru(III)], exhibits negative first-order reliance with respect to [HClO4], and shows first-order dependence on [NBS]. The observed constancy in oxidation rate with the inclusion of electrolyte suggests a zero salt effect. The fractional order reliance on 4-CBZ and Ru(III) suggests that the catalyst and substrate form a complex prior to the rate-determining step. The results demonstrate that the NBS itself and [RuCl5(H2O)]2− will be the most reactive species of NBS and Ru(III) in an acidic environment. The oxidation rate is markedly increased by Ru(III) (2.1 times) acting as a catalyst at ppm concentration. The micellar media of DTAB further accelerates the reaction rate by a factor of 4.3. Ru(III) and DTAB micelles synergistically enhanced the oxidation rate of 4-CBZ by 6.4 fold. A credible mechanism that corresponds with the kinetic findings has been emphasized, alongside an analysis of the Piszkiewicz model, to elucidate the apparent catalytic influence of DTAB micellar environments.