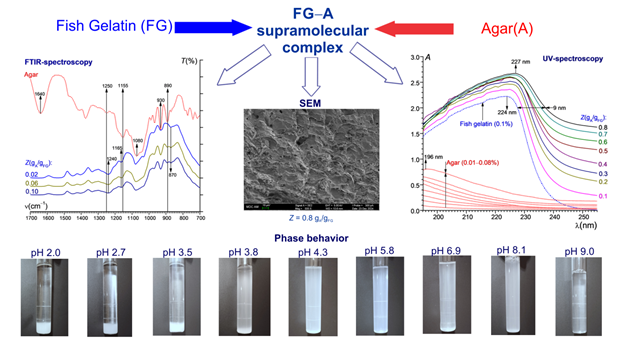
ФАЗОВОЕ СОСТОЯНИЕ ВОДНЫХ СМЕСЕЙ РЫБНЫЙ ЖЕЛАТИН–АГАР
Н. Г. Воронько, Т. Д. Кузина, Д. С. Колотова, Ю. А. Кучина, Ю. Ф. Зуев, С. Р. Деркач
Полный текст (PDF), 302 просмотров
Аннотация:
Аннотация. Методами спектроскопии (ИК Фурье, …
Аннотация. Методами спектроскопии (ИК Фурье, УФ), турбидиметрии, квазиупругого лазерного светорассеяния и сканирующей электронной микроскопии исследовано взаимодействие рыбного желатина и агара в объеме водной фазы с образованием супрамолекулярных белок–полисахаридных комплексов. Рассмотрено влияние строения желатина (содержание аминокислотных остатков), массового соотношения агар/рыбный желатин Z и среды (pH, ионная сила I) на границы областей формирования стехиометричных и нестехиометричных комплексов, размер и ζ-потенциал частиц и, следовательно, фазовое состояние водных смесей (коллоидных растворов) биополимеров. Построены фазовые диаграммы водных смесей агара и рыбного желатина в координатах Z – характеристические pH, а также I – характеристические pH. Определены области с различным фазовым состоянием систем: однофазный раствор не связанных в комплекс биополимеров, дисперсия комплексов рыбный желатин–агар, область начала выделения из дисперсии коацерватов, область полного разделения коацерватной фазы и супернатанта. Показано, что формирование комплексов рыбный желатин–агар оказывает воздействие на микроструктуру гелей, образованных при охлаждении водных смесей биополимеров.
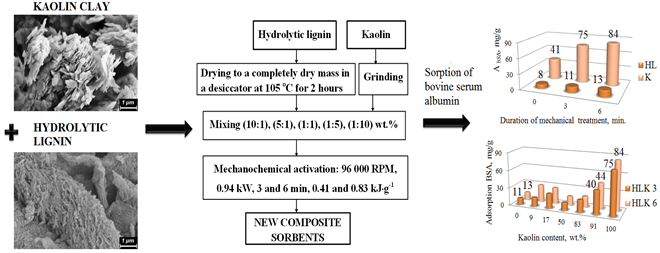
ВЛИЯНИЕ МЕХАНИЧЕСКОЙ АКТИВАЦИИ НА СТРУКТУРУ И СОРБЦИОННЫЕ СВОЙСТВА ГИДРОЛИЗНОГО ЛИГНИНА, КАОЛИНА И КОМПОЗИТОВ НА ИХ ОСНОВЕ
О. Н. Дабижа, Е. А. Бондаревич, Е. М. Иванькова, Т. В. Хамова, О. А. Шилова
Полный текст (PDF), 232 просмотров
Аннотация:
Для целенаправленного изменения структуры каолина …
Для целенаправленного изменения структуры каолина и повышения его сорбционной емкости был использован экспресс-метод сухой механохимии без растворителя путем тонкого измельчения на воздухе в течение 3 и 6 минут в мельнице (0.94 кВт; 26 000 об×мин–1). В том же процессе каолин был модифицирован гидролизным лигнином для гидрофобизации и улучшения его сорбционных свойств. Методами электронной микроскопии, рентгеновской дифракции, инфракрасной спектроскопии, низкотемпературной адсорбции азота, УФ-абсорбционной спектроскопии изучено влияние механической активации на структуру и свойства каолина, гидролизного лигнина и композитов на их основе с различными соотношениями компонентов. Плотная структура каолинита была сохранена, водородные связи в гидролизном лигнине были разрушены, количество карбонильных групп увеличилось, а фрагменты природного полимера были привиты к каолиниту. Было обнаружено, что в композитах образуется агрегационно-агломерационная микроструктура. Каолин, а также композит каолина и гидролизного лигнина с массовым соотношением 10 : 1, обработанные дозой механической энергии 0.83 кДж×г–1, продемонстрировали значительные изменения в структуре и достаточно высокие сорбционные характеристики. Удельная поверхность этих сорбентов по Брунауэру-Эмметту-Теллеру составила ~ 16 м2×г–1, адсорбция бычьего сывороточного альбумина – 83.63 и 44.10 мг×г–1 соответственно. Таким образом, сухая механическая активация на воздухе в «мягких» условиях позволила увеличить сорбцию бычьего сывороточного альбумина каолином на 104%.
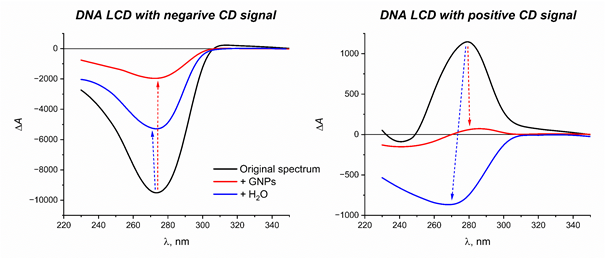
О НЕКОТОРЫХ ОСОБЕННОСТЯХ ВЗАИМОДЕЙСТВИЯ УЛЬТРАМАЛЫХ НАНОЧАСТИЦ ЗОЛОТА С ЖИДКОКРИСТАЛЛИЧЕСКИМИ МИКРОЧАСТИЦАМИ ДНК
М. А. Колыванова, М. А. Климович, А. В. Шибаева, О. В. Дементьева, В. М. Рудой, В. А. Кузьмин, В. Н. Морозов
Полный текст (PDF), 307 просмотров
Аннотация:
Исследованы особенности взаимодействия синтезированных по …
Исследованы особенности взаимодействия синтезированных по методу Даффа ультрамалых наночастиц золота (НЧЗ) с частицами оптически активных жидкокристаллических дисперсий (ЖКД) ДНК, сформированных при варьируемых концентрациях NaCl и полиэтиленгликоля. Показано, что влияние НЧЗ на ЖКД с положительной и отрицательной ориентацией аномального сигнала кругового дихроизма различается. По-видимому, это отчасти обусловлено разной конформацией молекул ДНК, образующих соответствующие дисперсные частицы. Обсуждаются также кинетические аспекты взаимодействия НЧЗ с ЖКД ДНК и особенности «загрузки» в частицы ЖКД ультрадисперсного золота.
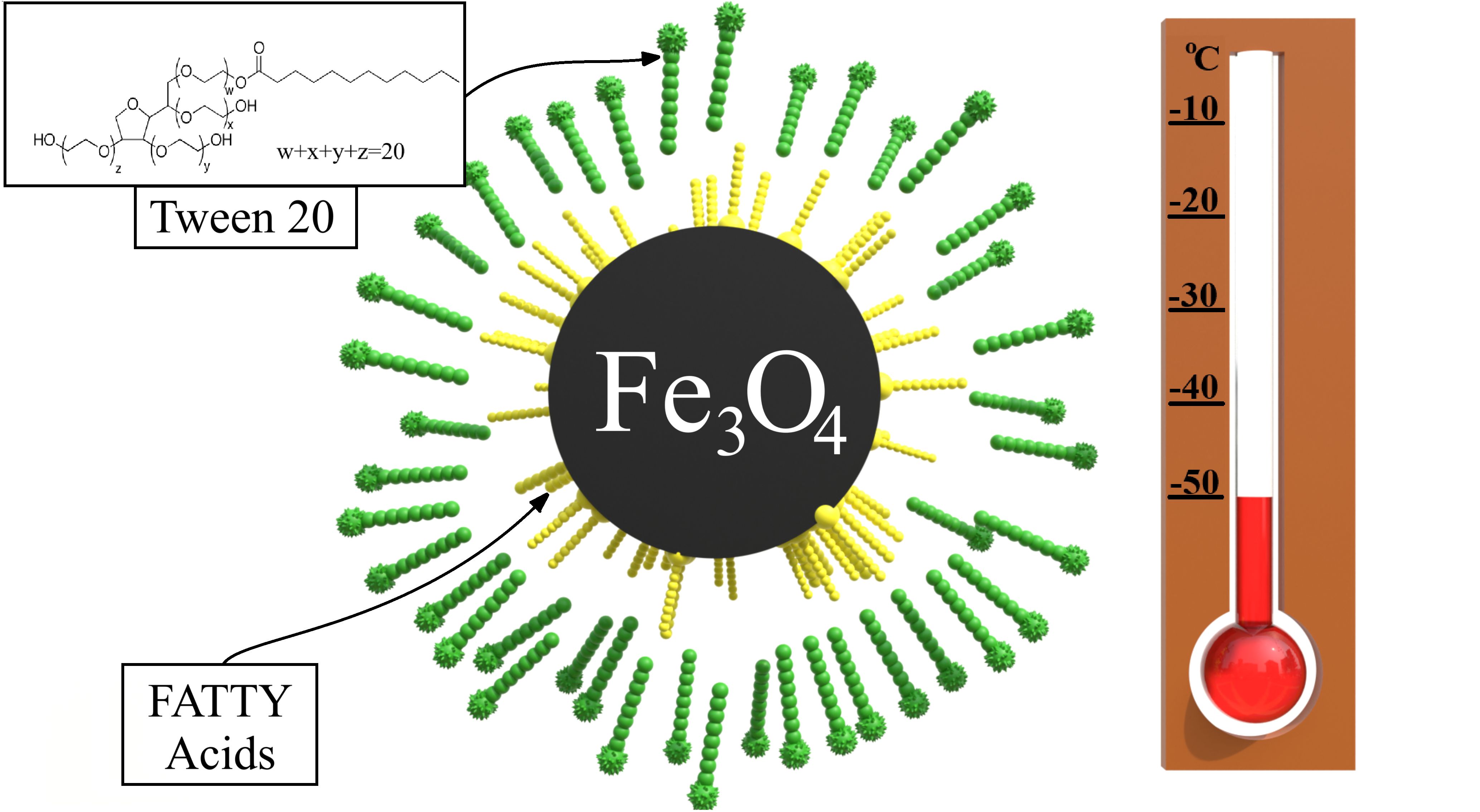
НИЗКОТЕМПЕРАТУРНЫЕ МАГНИТНЫЕ ЖИДКОСТИ НА БАЗЕ СПИРТОВЫХ И СОЛЕВЫХ РАСТВОРОВ, СТАБИЛИЗИРОВАННЫЕ ДВОЙНЫМ СЛОЕМ С НЕИОНОГЕННЫМ ПАВ ТВИН 20
А. В. Лебедев, С.Н. Лысенко
Полный текст (PDF), 276 просмотров
Аннотация:
Синтезированы образцы магнитной жидкости, стабилизированных …
Синтезированы образцы магнитной жидкости, стабилизированных двойным слоем ПАВ в воде с использованием неионогенного стабилизатора ТВИН 20 (Полисорбат 20) в качестве второго слоя. Исследованы реологические свойства синтезированных образцов в зависимости от их концентрации. В отличие от жидкостей с диссоциируемым ПАВом, с ростом температуры вязкость магнитной жидкости убывает быстрее, чем вязкость базовой среды (воды).
Главным преимуществом использования неионогенного ПАВа является возможность синтеза низкотемпературных магнитных жидкостей на основе водно-спиртовых смесей и водных растворов солей. Жидкости, стабилизированные ТВИН20 в растворах этиленгликоля и пропиленгликоля, сохраняют подвижность вплоть до температур -40°С и -50°С. При использовании в качестве базовой среды раствора хлорида кальция CaCl2, пробный образец жидкости сохранял работоспособность до температуры -30°С.
Магнитные жидкости на основе спиртовых и солевых растворов могут оказаться незаменимыми в областях техники, где предъявляются жесткие требования к их пожарной и экологической безопасности. Химическая пассивность частиц, стабилизированных ТВИН20, делает возможным их применение в биологии и медицине.
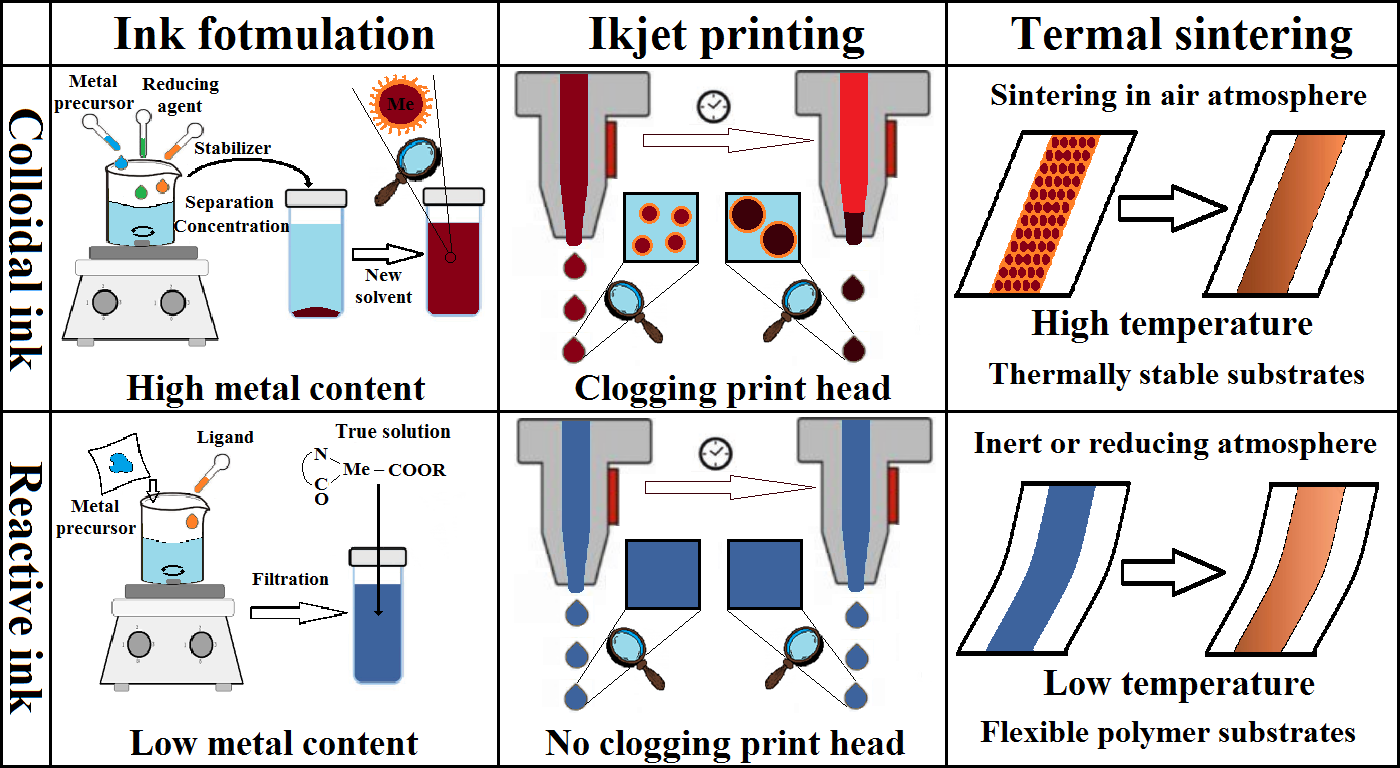
ЧЕРНИЛА ДЛЯ ПЕЧАТНОЙ ЭЛЕКТРОНИКИ НА МЕТАЛЛИЧЕСКОЙ ОСНОВЕ. СРАВНЕНИЕ ОСНОВНЫХ ПОДХОДОВ К ПОЛУЧЕНИЮ
П. С. Поповецкий
Полный текст (PDF), 402 просмотров
Аннотация:
Печатная электроника является бурно развивающимся …
Печатная электроника является бурно развивающимся направлением современной науки о материалах. Использование печатного оборудования может позволить значительно упростить и удешевить процесс получения пассивных и активных электронных компонентов. В данном направлении ежегодно публикуются десятки обзорных и сотни научных статей. Но при этом потребительские характеристики рецептур чернил для печатной электроники в той или иной мере компромиссные: улучшение одних свойств, как правило, приводит к ухудшению других. Например, увеличение содержания основного компонента обычно приводит к снижению стабильности.
В данном обзоре будут сопоставлены два основных подхода к получению чернил на металлической основе, которые можно условно назвать «металлорганическим» и «коллоидным», рассмотрены их сильные и слабые стороны и оценены перспективы дальнейшего развития печатной электроники.
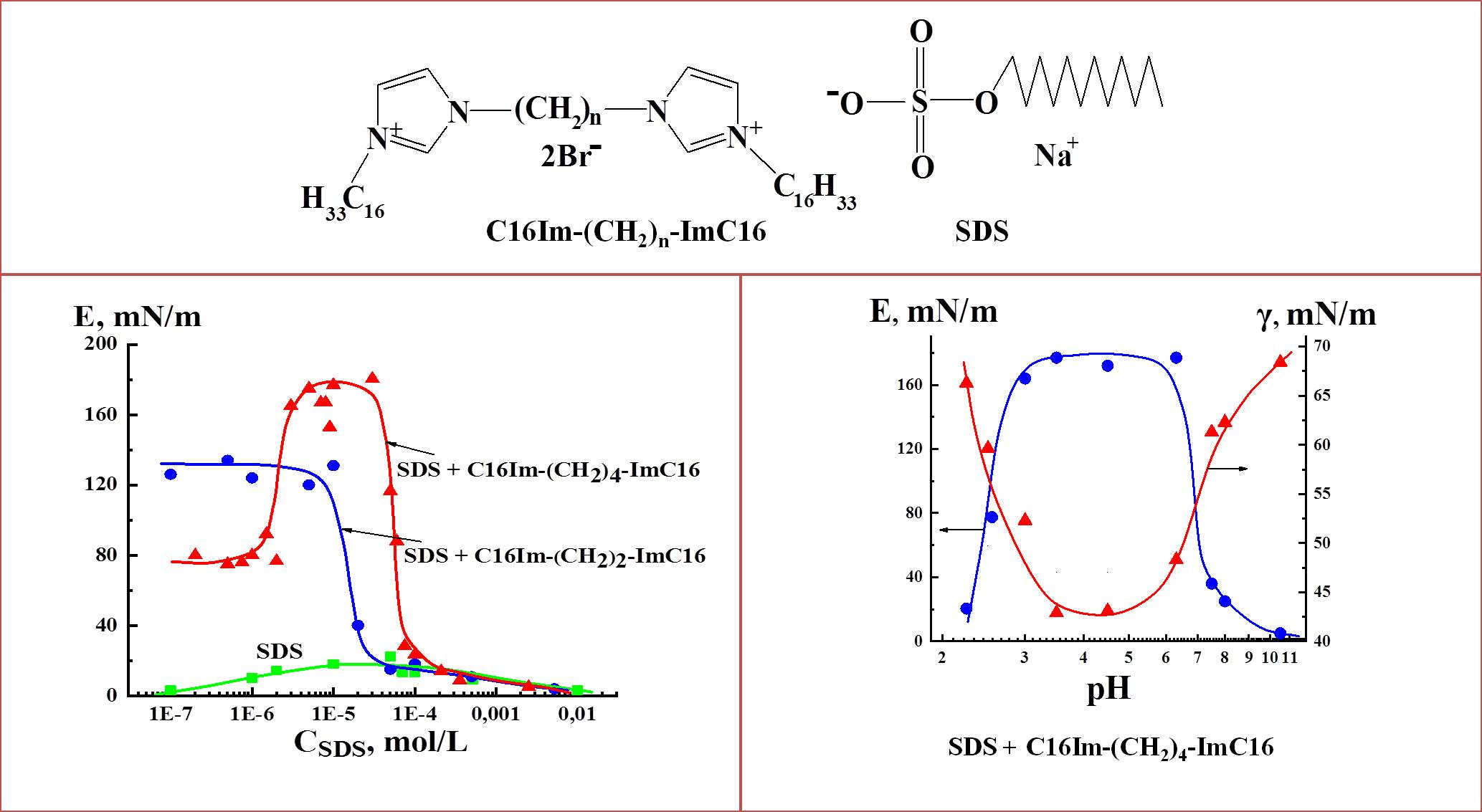
ВЛИЯНИЕ ДОБАВОК АНИОНАКТИВНЫХ ПАВ НА ПОВЕРХНОСТНЫЕ ХАРАКТЕРИСТИКИ РАСТВОРОВ ДИКАТИОННЫХ ДИИМИДАЗОЛИЕВЫХ ПАВ С КОРОТКИМИ МОСТИКОВЫМИ ФРАГМЕНТАМИ
С. Л. Хилько, А. А. Котенко
Полный текст (PDF), 248 просмотров
Аннотация:
Методами формы висячей капли и …
Методами формы висячей капли и осциллирующей капли исследованы тензиометрические и дилатационные реологические характеристики растворов смесей дикатионных диимидазолиевых поверхностно-активных веществ (ПАВ) с предельно короткими мостиковыми фрагментами и анионактивными ПАВ (додецилсульфат натрия, сульфонол, 3-лауретсульфат натрия) на границе раздела с воздухом. Характер взаимодействия дикатионных и анионактивных ПАВ зависит от структуры молекул АПАВ. Показана возможность образования прочных комплексов между дикатионным ПАВ с количеством метиленовых групп в мостиковом фрагменте равном 4 и додецилсульфатом натрия при соотношении компонентов близком к 1:1. Установлено, что образующиеся комплексы устойчивы в нейтральной и слабокислой области рН.
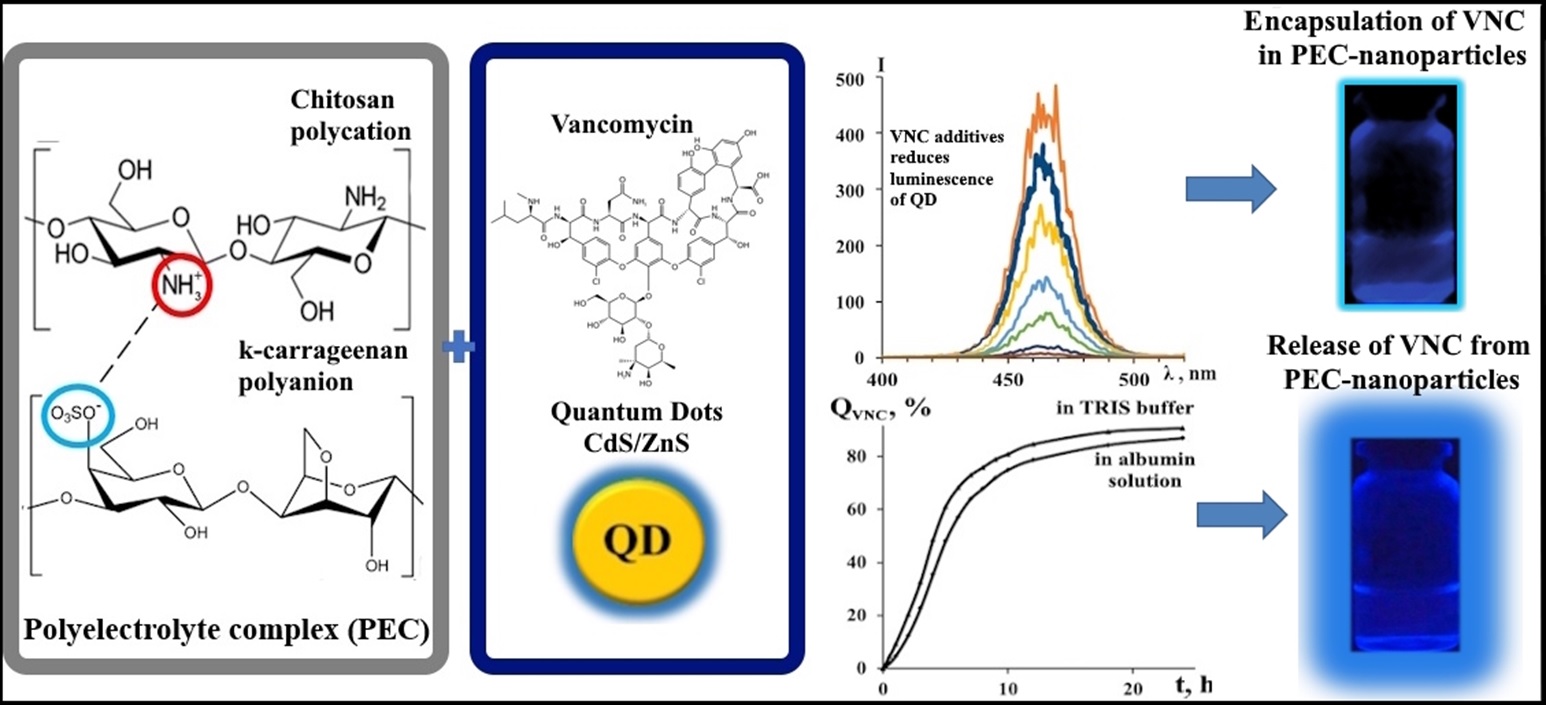
ЛЮМИНЕСЦЕНТНЫЕ НАНОЧАСТИЦЫ ПОЛИЭЛЕКТРОЛИТНОГО КОМПЛЕКСА ХИТОЗАНА С КАРРАГИНАНОМ КАК ПЕРСПЕКТИВНЫЕ МНОГОФУНКЦИОНАЛЬНЫЕ СИСТЕМЫ ДОСТАВКИ ВАНКОМИЦИНА
С. В. Шилова, Г. М. Миргалеев, Д. О. Сагдеев, Ю. Г. Галяметдинов
Полный текст (PDF), 309 просмотров
Аннотация:
Получены и охарактеризованы наночастицы полиэлектролитного …
Получены и охарактеризованы наночастицы полиэлектролитного комплекса хитозана с κ-каррагинаном, содержащие квантовые точки «ядро-оболочка» CdS/ZnS, как модели биосовместимых люминесцентных систем доставки антибиотика ванкомицина с эффективностью инкапсулирования 95–97%. Квантовые точки получены коллоидным методом синтеза и гидрофилизированы меркаптопропионовой кислотой. Изучено влияние ванкомицина, инкапсулированного в частицы полиэлектролитного комплекса, на люминесцентные свойства квантовых точек CdS/ZnS. Продемонстрированы возможности синтезированных квантовых точек в качестве модельных наносенсоров для определения включения и высвобождения ванкомицина из разработанных носителей на основе тушения люминесценции квантовых точек. Исследовано связывание ванкомицина с альбумином как моделью белка крови, определен состав комплекса ([ванкомицин] : [альбумин] = 1.0 : 2.0) и константа его устойчивости (βк=6.0∙104 М–1). Анализ кинетических данных высвобождения ванкомицина из полимерных носителей в условиях in vitro в растворы альбумина и трис-буфера в рамках математической модели Корсмейера–Пеппаса, показал, что высвобождение антибиотика контролируется как диффузией, так и релаксацией полимерной матрицы.
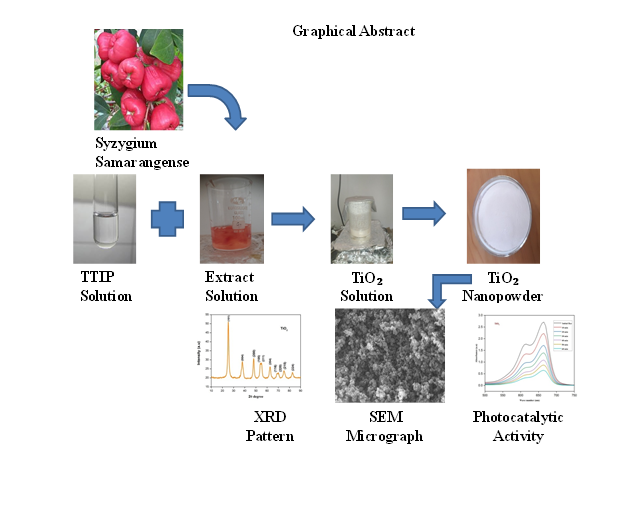
Biofabrication of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Using Syzygium samarangense Extracts: Characterization and Evaluation of their Photocatalytic Activity
Ganapathy Aarthe, PeriyasamyAnitha , Sivamaruthamuthu Nandhini
233 просмотров
Аннотация:
The research work presents, the …
The research work presents, the eco-friendly synthesis of titanium dioxide (TiO₂) nanoparticles using an aqueous extract of Syzygium samarangense through a green synthesis approach. The biofabricated TiO₂ nanoparticles were characterized using various techniques, including Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy, which revealed a distinctive ball-like morphology. The Crystalline size of nanomaterials were determined by X-ray diffraction method. Ultra Violet spectroscopy analysis indicates band gap energy of 3.1 eV, which confirms that nanoparticles is suitable for photocatalytic applications. Phytochemical analysis of the Syzygium samarangense extract demonstrated the presence of key biomolecules such as alkaloids and phenolic compounds, which likely played a crucial role in nanoparticles synthesis and stabilization. The photocatalytic activity of the synthesized TiO₂ nanoparticles was evaluated using methylene blue dye degradation under Ultra Violet light. The nanoparticles exhibited significant photocatalytic efficiency, with a marked decrease in methylene blue concentration over time, highlighting their potential for environmental remediation. These results demonstrate the viability of green-synthesized TiO₂ nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications, offering a sustainable alternative to conventional methods of nanoparticles fabrication.
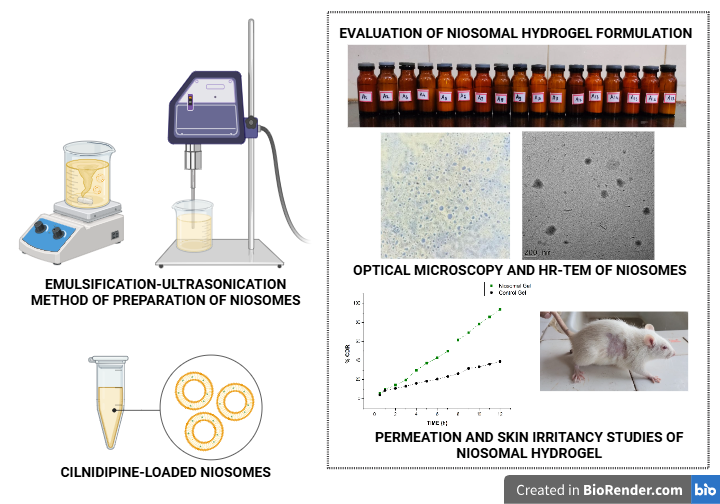
Cilnidipine-Loaded Niosomes: A Novel Transdermal Delivery System for Enhanced Permeation
A. A. Madhav, D. D. Kambli, C. E. M. DCruz, L. Kumar, R. K. Shirodkar
188 просмотров
Аннотация:
The objective of the study …
The objective of the study was to formulate Cilnidipine-loaded niosomes using cholesterol and Span 60 using the emulsification-ultrasonication method. The Box-Behnken design was adopted to optimize process variables in order to attain lower particle size and higher entrapment efficiency. Niosomal dispersion was evaluated for particle size, zeta potential, and entrapment efficiency. Morphological and drug release characteristics were also studied. The Cilnidipine niosomes were further developed as a hydrogel and evaluated for its physical appearance, viscosity, swelling characteristics, pH, spreadability, release characteristics permeation, skin irritation potential, and stability. The niosomes exhibited particle size in the range of 138.1 to 355.5 nm and drug entrapment of 82.63 to 91.77%. At the end of 8 hours, 89.06% of the drug was released. Morphological studies revealed the spherical nature of the niosomal vesicles. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, Differential scanning calorimetry, and X-ray diffractometry studies were also performed. Rat skin permeation studies showed a greater transdermal flux (0.4952 mg/cm².h) and permeation coefficient (0.09904) as compared to the control gel. Clove oil in cilnidipine niosomes acts as a vesicular membrane-fluidizing agent for greater drug delivery across the stratum corneum. This, along with Span 60, reduced the stratum corneum barrier rigidity, thereby enhancing its delivery across the skin. The present study thus demonstrated that Cilnidipine niosomal formulation could be a favourable transdermal delivery system for the treatment of hypertension.
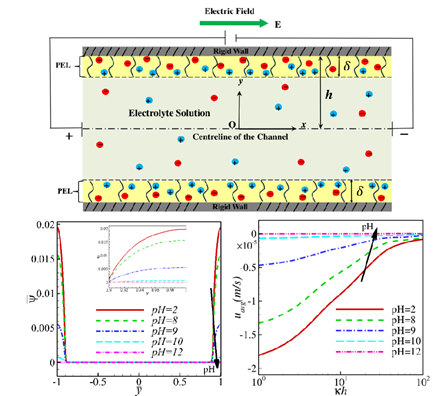
Ion Size and Ion Partitioning Effects on Electroosmosis Flow of Power-Law Fluids in pH-Responsive Soft Nanochannels with Basic Functional Groups
Amit Malick, Bhanuman Barman
154 просмотров
Аннотация:
This study numerically investigates …
This study numerically investigates the electroosmotic flow (EOF) of power-law fluids in soft nanochannels whose inner walls are coated with pH-sensitive polyelectrolyte layers (PELs) containing basic functional groups. We focused on the combined effects of ion size and ion partitioning on the fully developed EOF within these channels. Our model uses modified Poisson-Boltzmann and Cauchy momentum equations to describe the electrostatic potential and flow velocity, which we solved numerically using the finite difference method. The results highlight the significant influence of ion size and ion partitioning (due to permittivity differences between the PEL and electrolyte) on both the electrostatic potential and the flow velocity, along with the role of other key parameters. We also emphasize the importance of the basic functional group present throughout the PEL on the selectivity of mobile electrolyte ions.
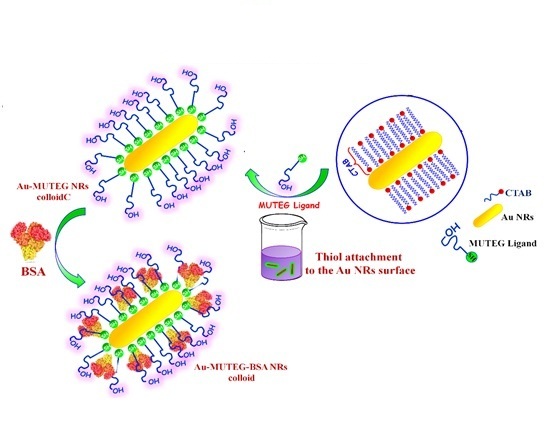
Functionalization of Gold Nanorods with Monohydroxy Thioalkylated PEG and Study of Their Cytotoxicity and BSA Adsorption
A. Salabat, F. Mirhoseini, P. Rezaei, F. Shayanmehr, D. Salabat
153 просмотров
Аннотация:
In this research, water-soluble functionalized …
In this research, water-soluble functionalized gold nanorods (Au NRs) with low toxicity were synthesized by a seed-mediated growth method. For this purpose, a seed solution of the gold nanoparticles was added to the growth solution containing a weak reducing agent to form a controlled size of gold nanorods. After that, to explore the applicability of gold nanoparticles in biomedicine, particularly in photothermal therapy as a noninvasive therapeutic tool, the prepared Au NRs were functionalized using (11-Mercaptoundecyl)tetra(ethylene glycol) as a monohydroxy thioalkylated PEG (MUTEG) ligand, for the first time. To confirm the formation of Au NRs and determination of their size and aspect ratio, UV-Vis spectroscopy and TEM techniques were applied. The CHNS analysis was employed to characterize the attached MUTEG ligands on the surface of the Au NRs. The HeLa cells were used to determine the cytotoxicity of the prepared Au-MUTEG NRs. The surface of the prepared Au-MUTEG NRs was conjugated with BSA to obtain Au-MUTEG-BSA NRs, as the final product, and confirmed by FT-IR analysis. The zeta potential analysis was also used to determine the charge and stability of the functionalized Au-MUTEG and Au-MUTEG-BSA NRs in comparison with Au NRs.
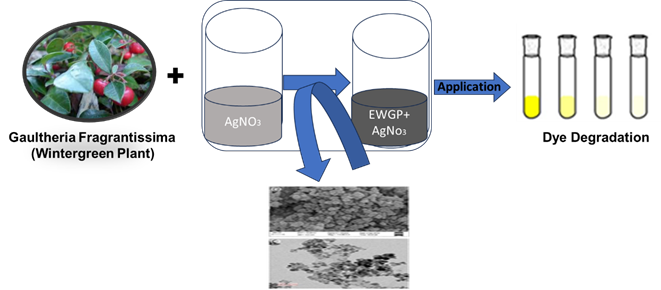
Adsorption Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using Wintergreen Plant Extract: A Green Approach to Dye Removal
Himanshu Singh, Raghvendra Singh Raghuvanshi, Abhishek Singh, Manorama Kumari Talla, Sajid Ali, Ritu Chauhan, Drashya Gautam
176 просмотров
Аннотация:
This study uses wintergreen (Gaultheria …
This study uses wintergreen (Gaultheria procumbens) plant extract as a reducing agent in a green synthesis technique to create silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). Numerous analytical methods, including scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), UV-visible spectroscopy, and zeta potential analysis, were used to characterize the synthesized AgNPs. The results revealed the successful synthesis of AgNPs with an average size of approximately 25 nm and a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystalline structure. Furthermore, the synthesized AgNPs effectively removed direct yellow 4 (DY4) dye from aqueous solutions, displaying a maximum adsorption capacity of 92 mg/g. The adsorption kinetics of DY4 on AgNPs followed the pseudo-second-order model, indicating that chemisorption mechanisms predominantly govern the adsorption process. Additionally, the adsorption isotherms of DY4 on the surface of AgNPs adhered closely to the Langmuir isotherm model, suggesting monolayer adsorption on the uniform surface of AgNPs through strong adsorbate-adsorbent interactions. Moreover, the AgNPs demonstrated promising potential for reusability, as evidenced by the retention of approximately 97% adsorption efficiency even after undergoing four consecutive adsorption-desorption cycles. This highlights the robustness and durability of the AgNPs as effective adsorbents for wastewater treatment applications.
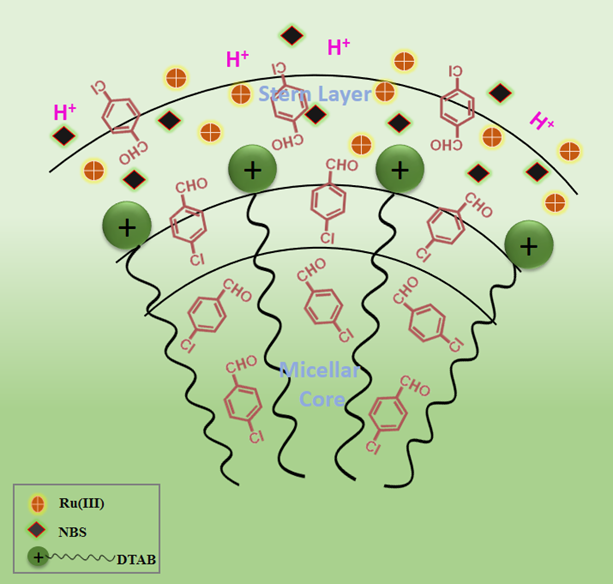
The Cumulative Impact of DTAB Micelles and Ru(III) on the Rate Augmentation of 4-Chlorobenzaldehyde by N-Bromosuccinimide
A. Srivastava, P.K. Pandey, N. Srivastava, R. K. Padhy, N. Srivastava
177 просмотров
Аннотация:
4-Chlorobenzoic acid (4-CBA) serves as …
4-Chlorobenzoic acid (4-CBA) serves as an important industrial compound, utilized as a probe for hydroxyl radicals in ozonation processes, as well as a ligand in the synthesis of luminescent lanthanide complexes. 4-CBA can be produced from 4-Chlorobenzaldehyde (4-CBZ) via oxidation using a specific oxidizing agent. The oxidation kinetics of 4-CBZ by N-Bromosuccinimide (NBS), facilitated by Ru(III), have been investigated in both the aqueous and dodecyltrimethylammonium bromide (DTAB) micellar medium. The reaction's progression was assessed by quantifying unreacted NBS iodometrically. Throughout the range of concentrations analyzed, the 4-CBZ oxidation demonstrates a fractional-order kinetics concerning both [4-CBZ] and [Ru(III)], exhibits negative first-order reliance with respect to [HClO4], and shows first-order dependence on [NBS]. The observed constancy in oxidation rate with the inclusion of electrolyte suggests a zero salt effect. The fractional order reliance on 4-CBZ and Ru(III) suggests that the catalyst and substrate form a complex prior to the rate-determining step. The results demonstrate that the NBS itself and [RuCl5(H2O)]2− will be the most reactive species of NBS and Ru(III) in an acidic environment. The oxidation rate is markedly increased by Ru(III) (2.1 times) acting as a catalyst at ppm concentration. The micellar media of DTAB further accelerates the reaction rate by a factor of 4.3. Ru(III) and DTAB micelles synergistically enhanced the oxidation rate of 4-CBZ by 6.4 fold. A credible mechanism that corresponds with the kinetic findings has been emphasized, alongside an analysis of the Piszkiewicz model, to elucidate the apparent catalytic influence of DTAB micellar environments.