Magnetite Nanoparticle Modified Pennisetum glaucum, an Eco-friendly, Efficient, and Low-cost Biosorbent for the Removal of Three Cationic Dyes from Waste Water
Aniket Singh, Anisha Grewal, Nishita Sharma, Partiksha Panghal, Sarita Yadav, Surender Kumar
Том 88 №1
145 просмотров;
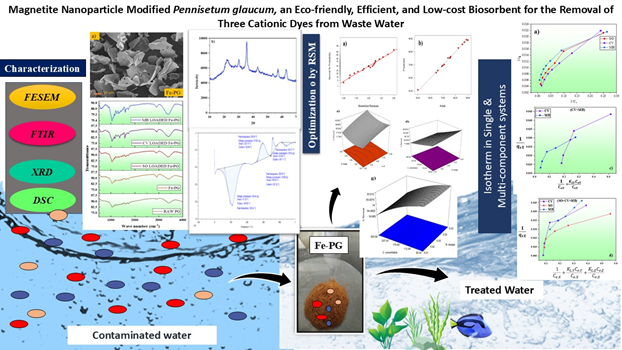
Modernization raised many concerns for environment, growing industrialization created major issues for fresh water bodies. In this study, magnetite nanoparticle modified Pennisetum glaucum was employed for the adsorptive removal of Crystal violet (CV), Safranine O (SO), and Mmethylene blue (MB) dye in single, binary and ternary system. The optimization of adsorption parameters was evaluated with the help of Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Adsorption kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamics study were employed to study the effect of time, concentration, and temperature respectively. Pseudo second order model was the best fitted kinetic model and Freundlich isotherm model was the best suited Isotherm model for all the three dyes. The qmax value (Maximum adsorption capacity) obtained from Langmuir model were 158.22 mg/g (SO), 217.39 mg/g (CV), and 122.10 mg/g (MB). The modified Langmuir isotherm model was explored to study the adsorption interaction mechanism in binary and ternary system. The competitive interactions between the co-existing dyes in the binary and ternary system resulted into the decreased maximum adsorption capacity. The adsorption mechanism was concluded as a result of electrostatic interactions, H-bonding, and pi-pi stacking. Overall, magnetite nanoparticle modified Pennisetum glaucum biosorbent can be helpful for reducing water pollution associated with dye pollutants.