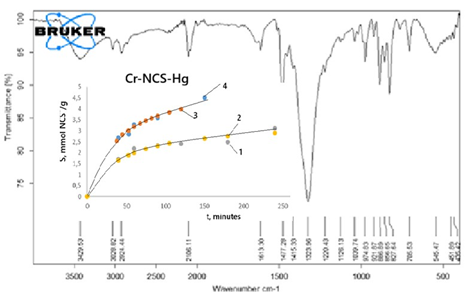
Sorption of thiocyanate ions on Cr-polymer composite and obtaining a new sorbent
V. Gutsanu, V. Costis
225 просмотров
Аннотация:
The sorption of thiocyanate ions …
The sorption of thiocyanate ions under various conditions on a Cr-polymer composite and, for comparison, on a strongly basic anion exchanger Purolite A-400(Cl) was studied. Temperature has a significant effect on sorption on the composite and a minor effect on Purolite A-40(Cl). The sorption of thiocyanate ions on both sorbents practically does not depend on the pH of the solution in the range 2-12. The rate of thiocyanate ion sorption is limited by mixed intra-particle and boundary layer diffusion. The sorption isotherms obtained at 18 and 60 oC on Purolite A-400 are well described by the Langmuir sorption model, and on the Cr-polymer composite – by the Freundlich model. The difference in the magnitude of sorption on these composites is explained by the fact that on Purolite A-400(Cl) the retention of thiocyanate ions occurs as a result of ion exchange, while on the Cr-polymer composite it occurs as a result of ion exchange and complex formation. The Cr-polymer composite loaded with thiocyanate ions becomes a sorbent with selective sorption properties in relation to heavy metal cations, which is confirmed by the retention of Hg2+ ions from solution.
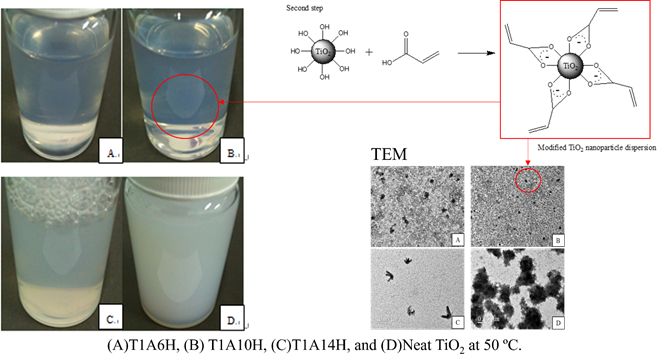
Enhanced Stability and Dispersion of Aqueous TiO2 Nanoparticles via Acrylic Acid Surface Modification
KuanLiang Liu, JinLin Han, KuoHuang Hsieh
163 просмотров
Аннотация:
Amorphous titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles …
Amorphous titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles were synthesized via a sol–gel reaction using titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) as the precursor. Acrylic acid (AA) was introduced to modify the particle surface, preventing aggregation and enabling functionalization. Fourier transform infrared analysis revealed that a reaction time of 48 hours was necessary to complete the surface modification through chelation and condensation. To optimize processing conditions, reactions were performed at 25 °C and 50 °C with varied TiO2: AA molar ratios. Results showed that at 50 °C, excessive AA (1:14) led to over-polymerization, while insufficient AA (1:6) failed to stabilize the particles. In contrast, the intermediate concentration (1:10) produced well-dispersed spherical nanoparticles (10-15 nm), as confirmed by dynamic light scattering (DLS) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). This study demonstrates that tuning AA concentration and reaction temperature enables kinetic control over surface modification, effectively stabilizing amorphous TiO2 in aqueous media. It offers a simple and scalable approach for preparing size-controlled, surface-functionalized amorphous TiO2 nanoparticles with potential optical and functional applications.
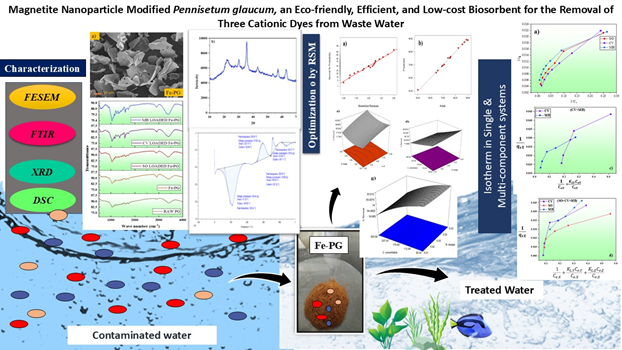
Magnetite Nanoparticle Modified Pennisetum glaucum, an Eco-friendly, Efficient, and Low-cost Biosorbent for the Removal of Three Cationic Dyes from Waste Water
Aniket Singh, Anisha Grewal, Nishita Sharma, Partiksha Panghal, Sarita Yadav, Surender Kumar
145 просмотров
Аннотация:
Modernization raised many concerns for …
Modernization raised many concerns for environment, growing industrialization created major issues for fresh water bodies. In this study, magnetite nanoparticle modified Pennisetum glaucum was employed for the adsorptive removal of Crystal violet (CV), Safranine O (SO), and Mmethylene blue (MB) dye in single, binary and ternary system. The optimization of adsorption parameters was evaluated with the help of Response Surface Methodology (RSM). Adsorption kinetics, isotherm, and thermodynamics study were employed to study the effect of time, concentration, and temperature respectively. Pseudo second order model was the best fitted kinetic model and Freundlich isotherm model was the best suited Isotherm model for all the three dyes. The qmax value (Maximum adsorption capacity) obtained from Langmuir model were 158.22 mg/g (SO), 217.39 mg/g (CV), and 122.10 mg/g (MB). The modified Langmuir isotherm model was explored to study the adsorption interaction mechanism in binary and ternary system. The competitive interactions between the co-existing dyes in the binary and ternary system resulted into the decreased maximum adsorption capacity. The adsorption mechanism was concluded as a result of electrostatic interactions, H-bonding, and pi-pi stacking. Overall, magnetite nanoparticle modified Pennisetum glaucum biosorbent can be helpful for reducing water pollution associated with dye pollutants.
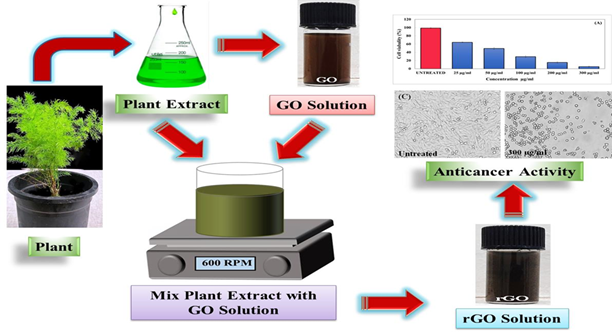
Green Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanosheets For In-Vitro Anticancer Activity
A. A. Survase, M. T. Mane, S. H. Sutar, , S. S. Desai, S. M. Mane, P. R. Salunkhe, A. C. Dike, S. B. Ubale, K. B. Pawar, V. S. Patil, N. T. Pandit, A. D. Kadam
109 просмотров
Аннотация:
Reduced graphene oxide nanosheets were …
Reduced graphene oxide nanosheets were synthesized using Asparagus officinalis (shatavari) leaves plant extract. Plant extract containing functional groups involvement in reduction of graphene oxide identified using functional group detection technique Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR). The pure crystal structure of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanosheets (NSs) was confirmed using X- ray diffraction (XRD) pattern. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed ultrathin graphene nanosheets morphology having thickness less than 7.5 nm. UV-Visible spectra of rGO shows absorption peak mainly at 279 nm. The elemental composition of rGO was studied by energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS) confirms phytochemical reduction graphene oxide (GO). Specific surface area rGO about 135 m2/g was measured by Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) technique. rGO NSs showed enhanced anticancer activity against human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231 tumour cells with 45 μg/ml. IC50 value emphasizing its role in biomedical field.
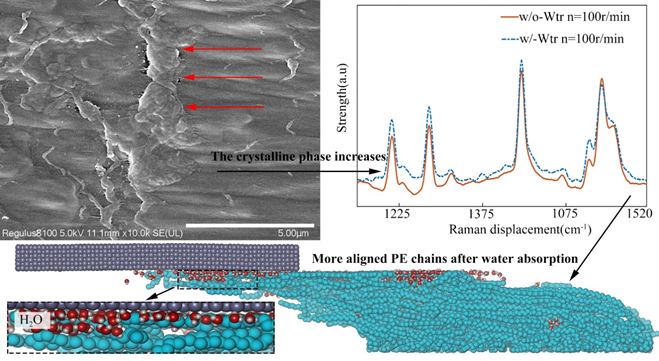
Tribological properties and microstructure changes of UHMWPE surface induced by water absorption
Linqiang Tao, Ting Zheng, Zicheng Jiang, Changle Sun
197 просмотров
Аннотация:
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) …
Ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) has become the preferred material for joint liners due to its excellent wear resistance and chemical stability. This study provides a basic investigation into how water absorption influences the tribological behavior and mechanical characteristics of UHMWPE. The surface plastic deformation layer formed during UHMWPE wear was found to exhibit significant changes after water absorption. Experimental results demonstrate that water absorption not only reduces the friction coefficient of the material by 7.79%, but also exacerbates plastic deformation, resulting in an increase of wear up to 4-fold compared to the control group. Raman spectroscopy analysis further confirmed a notable rise in surface crystallinity after water absorption. Indentation tests show water absorption decreases indentation depth. Molecular simulation results suggest that water absorption in UHMWPE chains tends to reduce the inter-molecular interactions and thereby facilitates the formation of ordered arrangements of surface polyethylene, leading to an anisotropic distribution, i.e., ordered alignment in parallel to the frictional direction, and anisotropic mechanical properties. The anisotropic distribution of surface polymer chains during friction, which was also strengthened after water absorption, in turn increases the resistance to indention. The investigation results of the tribological properties and mechanical characteristics of water-absorbed UHMWPE may provide useful insights for the evaluation and performance of artificial joints.
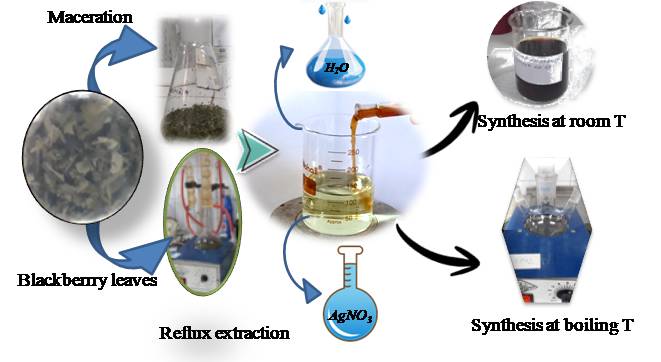
Characterization and Biological Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Stabilized by Aqueous Extracts of Rubus spp. Leaves
Marija S. Tasić, Jelena B. Zvezdanović, Ljiljana P. Stanojević, Jelena S. Stanojević, Sanja M. Petrović, BojanaDanilović, Dragan J. Cvetković
155 просмотров
Аннотация:
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs-E) biosynthesized at …
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs-E) biosynthesized at room and boiling T, stabilized by blackberry plant extracts (E) obtained by maceration at room T and reflux extraction at boiling T, are presented in this work. The obtained AgNPs-E were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), dynamic light scattering (DLS) and zeta potential measurement. XRD analysis confirmed that the 2θ peak at 38.2°, corresponding to the (111) plane, was the most intense, with the average crystallite size in the range of 18.0±3 − 21.1±2 nm. SEM spectroscopy showed that spherical shapes of nanoparticles dominate in the reaction mixture. EDX spectroscopy showed the presence of elemental silver in the formed AgNPs-E, along with the presence of C and Mg, which probably originate from the biomolecules of the extracts. DLS provides the size distribution with the average particle size in the range of 50.93±0.83 − 74.48±1.84 nm, with negative zeta potential ranged from -25.87±1.63 mV to -0.3027±0.36 mV indicating the AgNPs stability. The antimicrobial activity of AgNPs-E was tested by microdilution method confirming that both nanoparticles and extracts show the ability to inhibit all the bacteria and a fungus tested. The presented results suggest further investigations of synthesized AgNPs-E for application in topical cosmetic preparations.
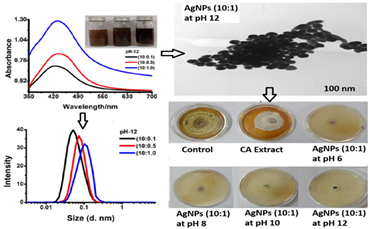
Eco-Responsive Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Chenopodium album: Influence of Environmental Parameters and pH
Swarnima Tiwari, Anirudh Srivastava, Malik Abdul Rub
141 просмотров
Аннотация:
This study reports …
This study reports the eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Chenopodium album (CA) leaf extract and evaluates their antifungal efficacy against Rhizoctonia solani. UV–Vis spectroscopy confirmed nanoparticle formation through pH- and extract volume-dependent red-shifts in surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peaks (405–435 nm), indicative of increased particle size and yield. Tauc plot analysis revealed a non-linear band gap variation (2.97 to 2.58 eV), reflecting quantum confinement effects influenced by pH. XRD patterns confirmed the crystalline nature and FCC structure of the AgNPs, while DLS and TEM analyses showed particle growth from 16.36 nm (pH 6) to 78.26 nm (pH 12), accompanied by morphological shifts and aggregation. Zeta potential values decreased from –30.92 mV to –14.75 mV, indicating reduced colloidal stability under alkaline conditions. In vitro assays demonstrated significant mycelial growth inhibition (MGI), with up to 91% suppression at pH 12 using 1.0 mL of CA extract. EC₅₀ values confirmed enhanced dose- and pH-dependent antifungal potency. Notably, seasonal and temporal cues critically shaped the biosynthesis of CA-AgNPs; spring in Meerut (25 °C, 55% RH) yielded ultra-small, stable particles (26 nm, SPR 410 nm) and peak antifungal performance (MGI 89%). These findings reveal how nature’s rhythm—via temperature, humidity, and harvest timing—can be harnessed to fine-tune nanoparticle functionality, presenting a promising green route for antifungal nanomaterial development.
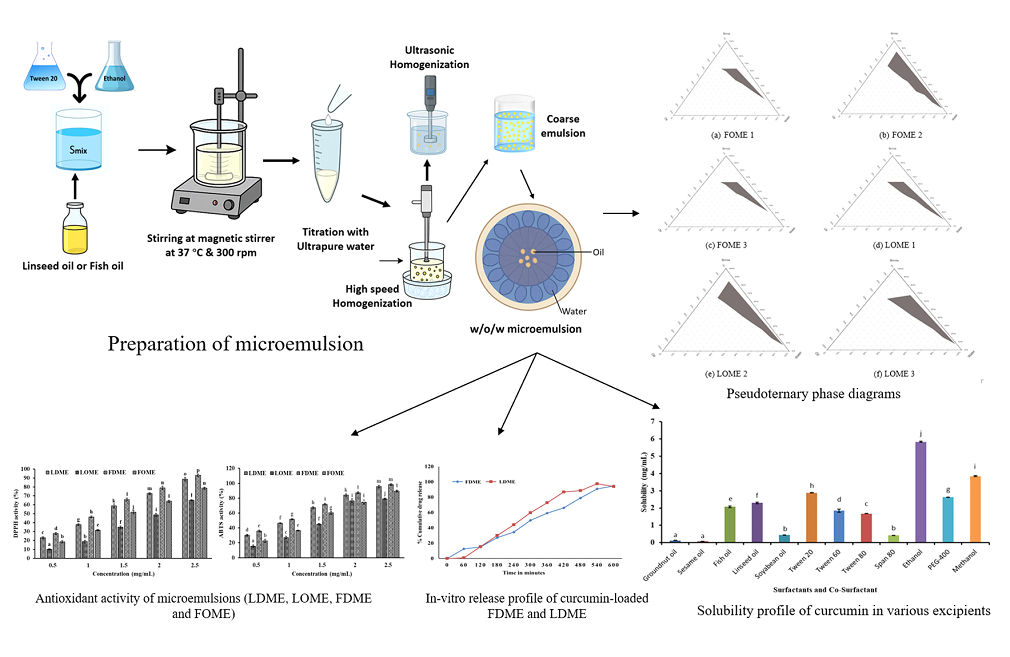
Exploring the Potential of Microemulsions with Curcumin loaded in Linseed and Fish Oils: Synthesis and Characterization
Priya Upadhyay, Anand Vaishnav, Anil Datt Upadhyay, Naresh Kumar Mehta
155 просмотров
Аннотация:
This study investigates the formulation …
This study investigates the formulation and characterization of curcumin-loaded microemulsions using linseed oil (LDME) and fish oil (FDME) to enhance the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of curcumin, a hydrophobic polyphenol with potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The microemulsions were prepared using Tween 20 as a surfactant and ethanol as a co-surfactant. The solubility of curcumin in linseed oil (2.301 mg/mL) and fish oil (2.078 mg/mL) were significantly (p < 0.05) higher compared to other oils, making them suitable carriers. Thermodynamic stability studies revealed that FDME formulations exhibited superior stability, with four out of ten formulations passing centrifugation, heating-cooling, and freeze-thaw cycles, while only two LDME formulations remained stable. Particle size analysis showed that curcumin-loaded FDME and LDME had mean diameters of 264.02 nm and 214.7 nm, respectively, with polydispersity indices (PDI) of 21.7% and 21.01%, indicating monodisperse distributions. Zeta potential values ranged from -11.3 mV to -17.8 mV, ensuring colloidal stability. Encapsulation efficiency was 97.05% for LDME and 93.95% for FDME, demonstrating effective curcumin retention. In vitro drug release studies revealed sustained release profiles, with LDME releasing 43.98% and FDME releasing 34.39% of curcumin over 3 hours, following zero-order kinetics. Antioxidant assays demonstrated enhanced ABTS and DPPH radical scavenging activities for curcumin-loaded microemulsions, with FDME showing 98.2% and LDME 95.63% ABTS inhibition at 2.5 mg/mL. These findings highlight the potential of curcumin-loaded microemulsions as effective delivery systems for improving the therapeutic efficacy of curcumin and omega-3 fatty acids in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical applications.