Eco-Responsive Biosynthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Chenopodium album: Influence of Environmental Parameters and pH
Swarnima Tiwari, Anirudh Srivastava, Malik Abdul Rub
Том 88 №1
141 просмотров;
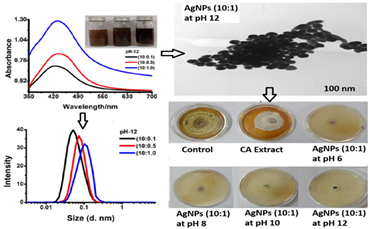
This study reports the eco-friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) using Chenopodium album (CA) leaf extract and evaluates their antifungal efficacy against Rhizoctonia solani. UV–Vis spectroscopy confirmed nanoparticle formation through pH- and extract volume-dependent red-shifts in surface plasmon resonance (SPR) peaks (405–435 nm), indicative of increased particle size and yield. Tauc plot analysis revealed a non-linear band gap variation (2.97 to 2.58 eV), reflecting quantum confinement effects influenced by pH. XRD patterns confirmed the crystalline nature and FCC structure of the AgNPs, while DLS and TEM analyses showed particle growth from 16.36 nm (pH 6) to 78.26 nm (pH 12), accompanied by morphological shifts and aggregation. Zeta potential values decreased from –30.92 mV to –14.75 mV, indicating reduced colloidal stability under alkaline conditions. In vitro assays demonstrated significant mycelial growth inhibition (MGI), with up to 91% suppression at pH 12 using 1.0 mL of CA extract. EC₅₀ values confirmed enhanced dose- and pH-dependent antifungal potency. Notably, seasonal and temporal cues critically shaped the biosynthesis of CA-AgNPs; spring in Meerut (25 °C, 55% RH) yielded ultra-small, stable particles (26 nm, SPR 410 nm) and peak antifungal performance (MGI 89%). These findings reveal how nature’s rhythm—via temperature, humidity, and harvest timing—can be harnessed to fine-tune nanoparticle functionality, presenting a promising green route for antifungal nanomaterial development.