Exploring the Potential of Microemulsions with Curcumin loaded in Linseed and Fish Oils: Synthesis and Characterization
Priya Upadhyay, Anand Vaishnav, Anil Datt Upadhyay, Naresh Kumar Mehta
Том 88 №1
155 просмотров;
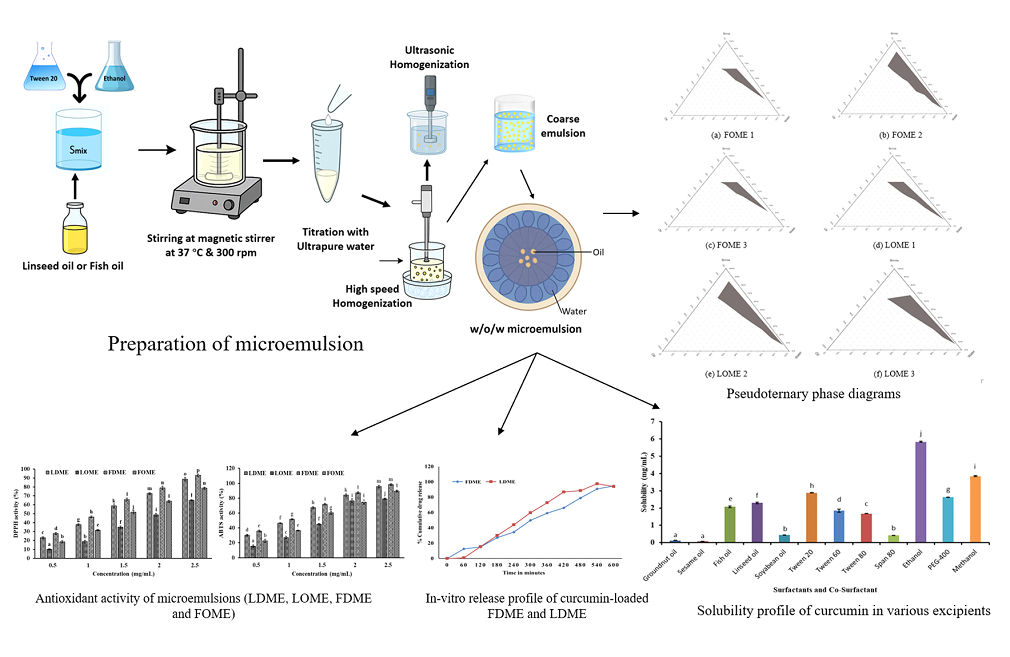
This study investigates the formulation and characterization of curcumin-loaded microemulsions using linseed oil (LDME) and fish oil (FDME) to enhance the solubility, stability, and bioavailability of curcumin, a hydrophobic polyphenol with potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The microemulsions were prepared using Tween 20 as a surfactant and ethanol as a co-surfactant. The solubility of curcumin in linseed oil (2.301 mg/mL) and fish oil (2.078 mg/mL) were significantly (p < 0.05) higher compared to other oils, making them suitable carriers. Thermodynamic stability studies revealed that FDME formulations exhibited superior stability, with four out of ten formulations passing centrifugation, heating-cooling, and freeze-thaw cycles, while only two LDME formulations remained stable. Particle size analysis showed that curcumin-loaded FDME and LDME had mean diameters of 264.02 nm and 214.7 nm, respectively, with polydispersity indices (PDI) of 21.7% and 21.01%, indicating monodisperse distributions. Zeta potential values ranged from -11.3 mV to -17.8 mV, ensuring colloidal stability. Encapsulation efficiency was 97.05% for LDME and 93.95% for FDME, demonstrating effective curcumin retention. In vitro drug release studies revealed sustained release profiles, with LDME releasing 43.98% and FDME releasing 34.39% of curcumin over 3 hours, following zero-order kinetics. Antioxidant assays demonstrated enhanced ABTS and DPPH radical scavenging activities for curcumin-loaded microemulsions, with FDME showing 98.2% and LDME 95.63% ABTS inhibition at 2.5 mg/mL. These findings highlight the potential of curcumin-loaded microemulsions as effective delivery systems for improving the therapeutic efficacy of curcumin and omega-3 fatty acids in nutraceutical and pharmaceutical applications.