ВЛИЯНИЕ УСЛОВИЙ ПОЛУЧЕНИЯ ДЕТОНАЦИОННОГО НАНОАЛМАЗА НА СОСТАВ ПОВЕРХНОСТИ И УСТОЙЧИВОСТЬ ЕГО ВОДНЫХ ЗОЛЕЙ
А. В. Волкова, Д. А. Савельев, Н. С. Чуйков, В. А. Водолажский, Л. Э. Ермакова
Полный текст (PDF), 623 просмотров
Аннотация:
В настоящей работе проведено …
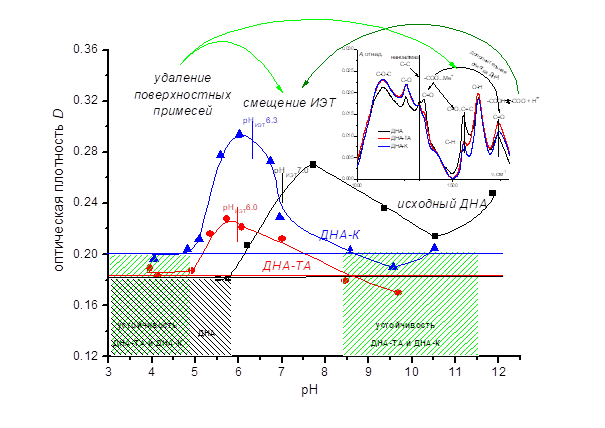
В настоящей работе проведено исследование влияния дополнительной обработки порошка детонационного наноалмаза (ДНА) базовой очистки на состав поверхности частиц ДНА, их электрокинетические свойства, а также агрегативную устойчивость в растворах индифферентного электролита (NaCl) в широком диапазоне рН. Установлено, что более высокая степень очистки образцов и увеличение количества протонированных карбоксильных групп на поверхности частиц ДНА вследствие дополнительной кислотной и термоаммиачной обработки приводит к смещению положения изоэлектрической точки (ИЭТ) от рН 7.0 для исходного образца до рН 6.3 и рН 6.0, соответственно. Показано, что величины порогов коагуляции гидрозолей при естественном рН и положение зон устойчивости в 10-3 М растворе хлорида натрия находятся в полном соответствии со значениями ИЭТ. Наибольшие пороговые значения при рН 5.8 наблюдаются для исходного ДНА, тогда как для дисперсии частиц ДНА после термоаммиачной обработки быстрая коагуляция протекает уже при концентрации 10-4 М. Показано также, что зоны агрегативной устойчивости для дополнительно обработанных образцов ДНА практически совпадают. В случае ДНА базовой очистки зона устойчивости в области положительных значений дзета-потенциала расширяется, а в области отрицательных значений устойчивости не наблюдается, вероятно, вследствие частичного растворения поверхностных примесей при высоких рН и перехода их в ионной форме в раствор, что вызывает коагуляцию частиц ДНА.
ЭЛЕКТРОКОНВЕКЦИЯ ОКОЛО ДВУХСЛОЙНЫХ КОМПОЗИТНЫХ МИКРОЧАСТИЦ
Г. С. Ганченко, В. С. Шелистов, Е. А. Демёхин
Полный текст (PDF), 632 просмотров
Аннотация:
В работе представлены результаты численного …
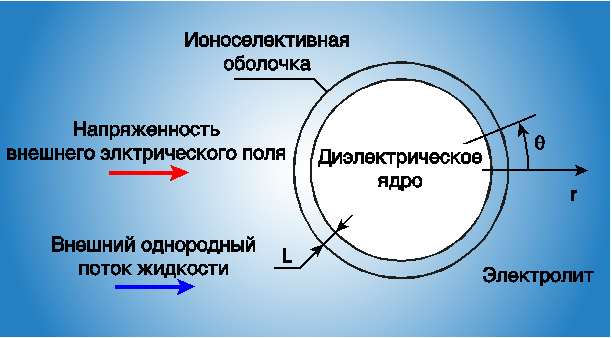
В работе представлены результаты численного моделирования поведения раствора электролита около сферической диэлектрической микрочастицы, покрытой однородной ионоселективной оболочкой, во внешнем электрическом поле. Предполагается, что частица зафиксирована, а электролит в отсутствие электрического поля покоится или движется с постоянной скоростью за счёт внешнего механического воздействия. Электрическое поле, в свою очередь, вызывает электроосмотическое движение электролита около частицы. Показано, что около такой композитной частицы может наблюдаться концентрационная поляризация, но электрокинетическая неустойчивость возникает лишь при достаточно большой толщине оболочки. Около частиц с поверхностным зарядом, противоположным заряду оболочки, могут наблюдаться нестационарные режимы течения, которые реализуются при небольшой толщине оболочки.
ПОЛИМЕРНЫЕ ГЕЛИ СФЕРИЧЕСКОЙ ФОРМЫ, СОДЕРЖАЩИЕ СУЛЬФОНАТНЫЕ ГРУППЫ: СИНТЕЗ И АДСОРБЦИОННЫЕ СВОЙСТВА
C. Г. Лаишевкина, Л. М. Друян, О. Д. Якобсон, Е. М. Иванькова, Б. М. Шабсельс, Н. Н. Шевченко
Полный текст (PDF), 682 просмотров
Аннотация:
Синтезированы пористые сшитые полиэлектролитные микросферы …
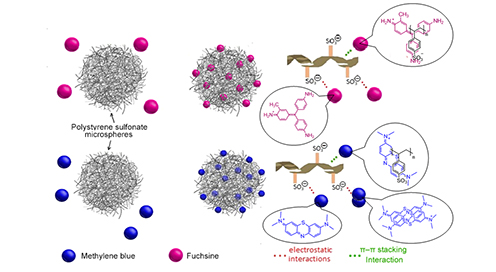
Синтезированы пористые сшитые полиэлектролитные микросферы диаметром от 1 до 5 мкм либо с применением в качестве функционального мономера пара-стиролсульфоната, либо смеси сомономеров пара-стиролсульфоната и винилацетата. Содержание сульфонатных групп в полученных полиэлектролитных микросферах составляет более 2 ммоль/г. Показано, что введение гидрофобного сомономера существенно увеличивает степень набухания полиэлектролитных микросфер. Найдено, что величина адсорбции модельных соединений (фуксин, метиленовый синий) превышает концентрацию сульфонатных групп. Морфология, структура поверхностного слоя полиэлектролитных микросфер изучены методом оптической и растровой электронной микроскопии, ИК-спектроскопии, удельная поверхность определена методом БЭТ.
Аннотация:
Рассмотрена стабилизация объемных нанопузырей при …
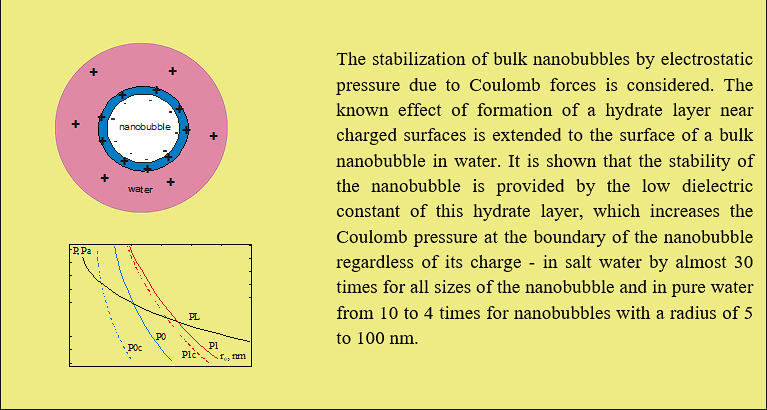
Рассмотрена стабилизация объемных нанопузырей при балансе на их границе давления Лапласа за счет поверхностного натяжения и электростатического давления за счет кулоновских сил. Учтено наличие гидратного слоя толщиной ~1 нм с касательной ориентацией диполей воды вокруг него, низкая диэлектрическая проницаемость которого, примерно равная 3, повышает давление на границе нанопузыря. Определены размеры и заряд стабильного нанопузыря. Показано, что в соленой воде гидратный слой независимо от заряда нанопузыря повышает давление на его границе почти в 30 раз, а в пресной – от 10 до 4 раз.

РЕОЛОГИЯ СТРУКТУРИРОВАННЫХ ЖИДКОСТЕЙ. РЕЖИМЫ ТЕЧЕНИЯ И РЕОЛОГИЧЕСКИЕ УРАВНЕНИЯ
В. Н. Матвеенко, Е. А. Кирсанов
Полный текст (PDF), 735 просмотров
Аннотация:
Представлена система реологических уравнений, …
Представлена система реологических уравнений, полученная на основе структурно-кинетических представлений, которая описывает вязкие и упругие свойства структурированных жидкостей, а именно, концентрированных суспензий, эмульсий, мицеллярных растворов, растворов и расплавов полимеров. Уравнения структурной модели справедливы для равновесного стационарного течения и для равновесного осциллирующего течения. Уравнения пригодны для аппроксимации реологических кривых на отдельных интервалах скорости сдвига или частоты колебаний. Каждому такому интервалу соответствует определенное состояние структуры. В качестве примера приведены результаты аппроксимации кривых сдвиговой вязкости для полимерного раствора, мицеллярного раствора и эмульсии.
ГЕНЕРАЦИЯ ЛАТЕКСНЫХ ЧАСТИЦ И ФАЗООБРАЗОВАНИЕ В ГЕТЕРОГЕННОЙ СТАТИЧЕСКОЙ СИСТЕМЕ МОНОМЕР-ВОДА
А. А. Оганесян, Г.К. Григорян, А.Г. Надарян, Н.Г. Григорян
Полный текст (PDF), 626 просмотров
Аннотация:
Целью данной работы является поиск …
Целью данной работы является поиск новых путей синтеза латексов (полимерных суспензий) с заданным размером и структурой поверхности частиц. Потребность в таких латексах не является масштабной, но их разработка и производство крайне важны для развития высоких технологий. Монодисперсные латексы особенно ценны в иммунологической диагностике широкого спектра заболеваний.
В статье представлены результаты исследований зарождения латексных частиц в гетерогенной системе мономер-вода. Результаты этих исследований позволили найти условия воспроизводимого синтеза монодисперсных полистирольных латексов.
С целью изменения поверхностной структуры латексных частиц в исходной мономерной фазе (стироле) растворяли цетиловый спирт. В статье представлены результаты электрон - микроскопических исследований синтезированных латексов. На поверхности латексных частиц отчётливо видны нанокристаллы этого спирта. Сделано предположение, что, при глубоких конверсиях мономера, в полимерно - мономерных частицах начинается процесс кристаллизации цетилового спирта.
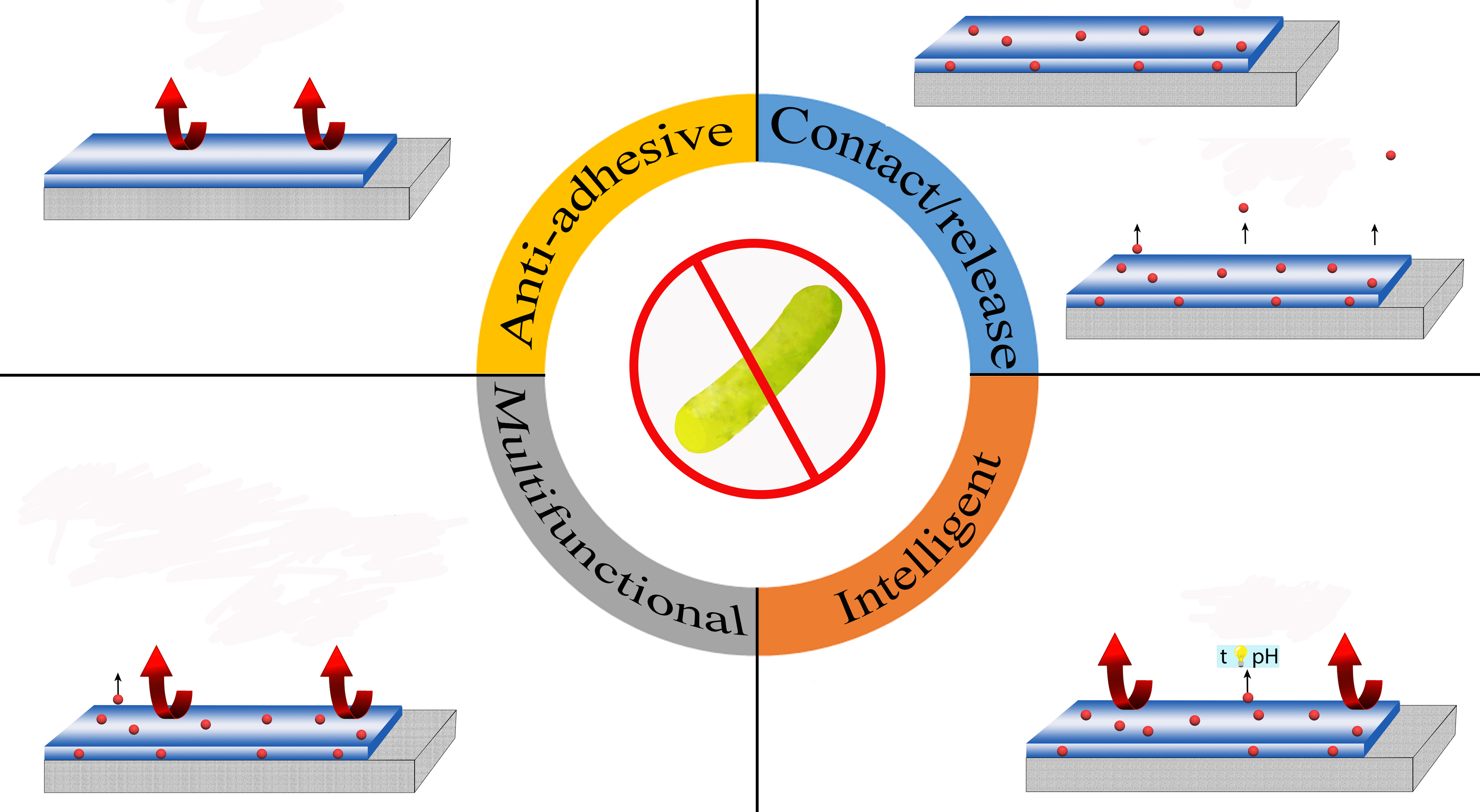
МОДИФИКАТОРЫ ПОВЕРХНОСТЕЙ ДЛЯ СНИЖЕНИЯ БАКТЕРИАЛЬНОЙ ОБСЕМЕНЕННОСТИ В МЕДИЦИНЕ И ПИЩЕВОЙ ПРОМЫШЛЕННОСТИ
Чередниченко Ю.В., Ишмухаметов И.Р., Фахруллина Г.И.
Полный текст (PDF), 526 просмотров
Аннотация:
Антибактериальные покрытия находят применение в …
Антибактериальные покрытия находят применение в пищевой и текстильной промышленности, в строительной отрасли, в биотехнологии и медицине. В обзоре рассмотрены основные виды покрытий, которые предотвращают обрастание биомакромолекулами и микроорганизмами: антиадгезивные, контактные, на основе релиза, многофункциональные и интеллектуальные («умные») покрытия. Для каждого вида покрытия описаны наиболее актуальные и эффективные действующие вещества, и механизм их действия. Несмотря на широкое распространение антиадгезионных поверхностей и покрытий контактного типа, они имеют множество недостатков, которые ограничивают сферы их применения и снижают активность и долговечность. Многочисленные исследования показывают, что многофункциональные и интеллектуальные покрытия имеют высокий потенциал для практического применения и дальнейших исследований по их модификации для получения универсальных и экономически выгодных покрытий. Основной проблемой практического применения таких поверхностей является несовершенство методов оценки стабильности и антибактериальных свойств покрытия в лабораторных условиях.
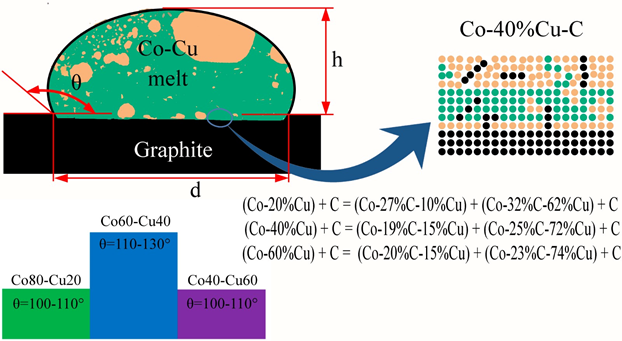
КИНЕТИКА ВЗАИМОДЕЙСТВИЯ РАСПЛАВОВ Co-Cu С ГРАФИТОМ И МИКРОСТРУКТУРА ОБРАЗУЮЩИХСЯ МЕТАЛЛ-УГЛЕРОДНЫХ КОМПОЗИЦИЙ
О. А. Чикова, И. Г. Ширинкина, В. С. Цепелев, Н. И. Синицин, В. В. Вьюхин
Полный текст (PDF), 759 просмотров
Аннотация:
Измерены временные зависимости контактного угла …
Измерены временные зависимости контактного угла и диаметра пятна смоченной поверхности при взаимодействии расплавов Co-Cu с содержанием меди 20, 40 и 60 ат. % с графитом при температурах 1390, 1440, 1490, 1540 и 1590°C. Смачивания графита расплавами Co-Cu в этих условиях не происходит: конечный контактный угол для Co80Cu20 - 95°, Co60Cu40 - 110°, Co40Cu60 - 100°. Конечное значение диаметра пятна смоченной поверхности при этом незначительно увеличивается. Металлографический анализ микроструктуры композиционных материалов Co-Cu-С, полученных путем контактного легирования расплавов Co-Cu углеродом показал зависимость морфологии структурных составляющих и фазового состава образцов от содержания меди. Композиционные материалы (Co-27%С-10%Cu) + (Co-32%С-62%Cu) + С и (Co-19%С-15%Cu) + (Co-25%С-72%Cu) + С, полученные при взаимодействии расплавов Co-Cu с содержанием меди 20, 40 ат.% с графитом, имеют макро однородную структуру.
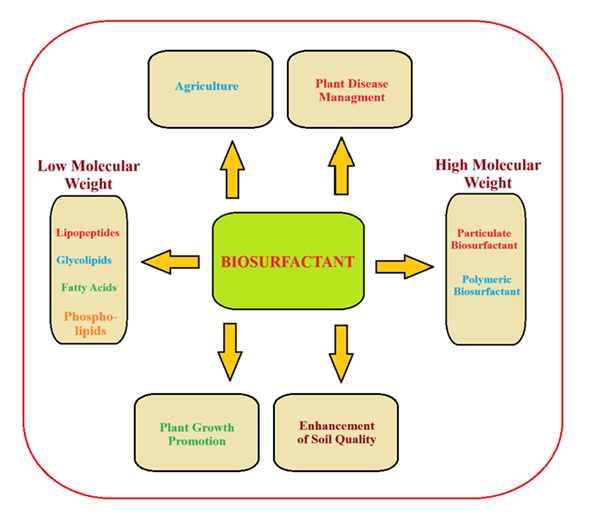
Amino Acid-Based Biosurfactants: Promising and Ecofriendly Biomolecules for Attaining Sustainable Agriculture and Environmental Safety
Nizamul Haque Ansari, Shumaila Shahid, Mohd Shoeb Khan, Navaid Zafar Rizvi, S. M. Shakeel Iqubal, Amal Bahafi
299 просмотров
Аннотация:
Biosurfactants are one of the …
Biosurfactants are one of the recently investigated biomolecules that have enormous applications in many fields including agriculture. As there is a need to develop less toxic, and environmentally friendly surfactants, therefore, amino-acid-based biosurfactants that are produced from renewable raw materials are of great demand nowadays and can be used as an alternative to conventional chemical surfactants. The negative effects of chemical surfactants present in agrochemicals and modern detergents can damage human health and the environment, thus there is a crucial requirement to explore innovative, well planned, as well as cost-effective natural products for the welfare of humanity. Biodegradable surfactants created through green chemistry, specifically amino acid-based surfactants (AABS), are a favourable alternative to avoid these risks. Since amino acids (AAs) are inexhaustible compounds, therefore biosurfactants based on AAs have abundant potential as eco-friendly.and environmentally friendly substances. Their higher biodegradation ability, low or even no toxicity, temperature stability, and tolerance to pH fluctuations make these biosurfactants preferable over chemical surfactants. In modern agriculture, most chemical pesticides and fertilizers used are frequently associated with numerous environmental issues. Hence, the development of green molecules as biosurfactants has a promising role in this regard to ensure agricultural sustainability. Biosurfactants can be harnessed for plant pathogen management, plant growth elevation, improving the quality of agricultural soil by soil remediation, degradation of complex hydrocarbons, increasing bioavailability of nutrients for advantageous plant-microbe interactions, and improving plant immunity, hence, they can supersede the grim synthetic surfactants which are presently being used.
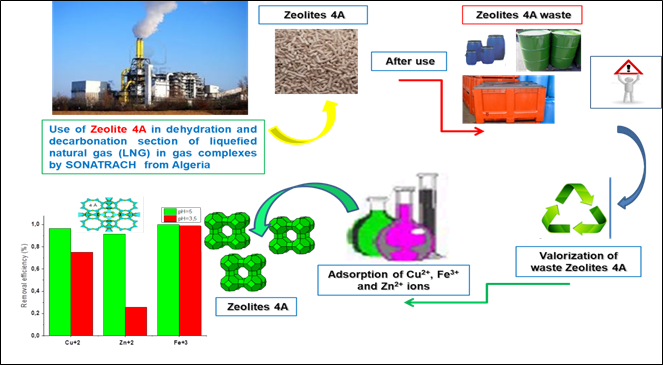
Adsorption of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Fe3+ Ions in a Ternary System from Aqueous Solutions on Industrial Waste 4A Zeolite: Characterization, Dynamic, Kinetic and Thermodynamic Studies
S. Bensafi, S. Amokrane, D. Nibou
288 просмотров
Аннотация:
The adsorption of Cu2+, Zn2+ …
The adsorption of Cu2+, Zn2+ and Fe3+ ions in a ternary system on waste zeolite 4A was examined under various experimental conditions (concentration, pH, Solid liquid ratio and temperature).The physicochemical and micro structural characterization (X-ray Diffraction, Scanning Electron Microscopy, Brunauer–Emmett–Teller, Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy, X-ray Fluorescence, Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy and Thermogravimetry/Differential Thermal Analysis) techniques were applied. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy was highlighted the bands characteristic of functional groups Me-(H2O), O-H (H2O), C-O, Me-Si-OH, Me-O and Si-OH of 4A and adsorbed by Cu2+, Fe3+ and Zn2+ ions (CFZ4A). The nature and coordination environment of these species were demonstrated by Ultraviolet-Visible Spectroscopy. The results show that the experimental adsorption capacities of the studied ions in the ternary system were respectively 79.125, 47.207 and 95.185 mg/g for Cu2+, Zn2+ and Fe3+. Temkin, Dubinin-Radushkevich and Freundlich equilibrium models give the best fit for the Cu2+, Zn2+ and Fe3+ ions according to R2 and the minimum values of Akaike information criteria. Elovich and Double exponential kinetics models are most appropriate to describe the adsorption data of Cu2+ and Zn2+ ions and Johnson-Mehl-Avrami model describes well the Fe3+ ions. The increase in temperature leads to a decrease in the free energy which indicates that the reaction is spontaneous and more favorable at high temperatures. The fixation of copper, zinc and iron ions in a ternary system on the waste of commercial zeolite 4A shows certain selectivity according to the following order: Fe3+> Cu2+>Zn2+.
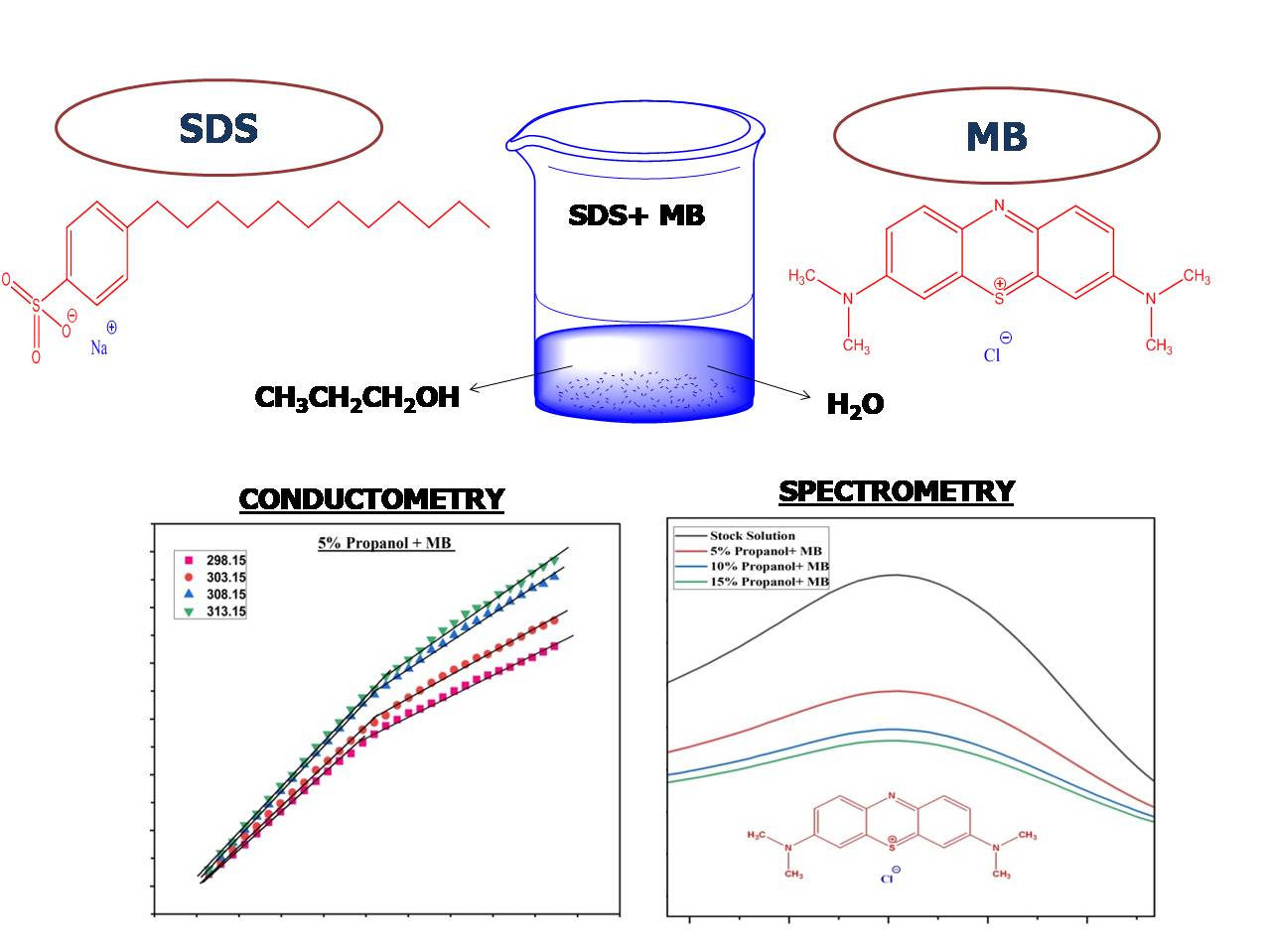
Investigation of Micellization and Spectrophotometric Study on the Interaction between Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate and Methylene Blue in Propanol- Water Mixed Solvent Media
Bharti Budhalakoti, Bhavana Agarwal, Pooja Sharma, N C Kothiyal
297 просмотров
Аннотация:
The study examines the micellization …
The study examines the micellization of Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) with methylene blue in a propanol-water mixed solvent system within a temperature spanning from 298.15 K- 313.15 K. The conductivity measurements of SDS- MB complex was carried out at 5%, 10%, and 15% volume fraction of propanol in water both in absence and presence of dye. The variation of CMC with temperature was analyzed to assess thermodynamic parameters of micellization. This approach offers valuable insights on the behavior of surfactant in mixed solvent system and sheds lights on different interactions occurring within the system. Spectrophotometric analysis was conducted to investigate the interactions between SDS- MB complex at 5%, 10%, and 15% volume fraction of propanol in aqueous medium. An increment in volume fraction of propanol hinders the process of micellization. However, in the presence of MB increases the efficiency of micellization and rendering the process more spontaneous. Consequently, MB monomers become associated with micelle which is the case of dye solubilization.
Preparation and properties of fluorine modified butyl acrylate/methyl methacrylate/ vinyl acetate/ tertiary vinyl carbonate quaternary polymer latex
Zheqing Gong, Lijun Chen
325 просмотров
Аннотация:
Acrylate polymer latex and vinyl …
Acrylate polymer latex and vinyl acetate-tert-carbonatepolymer latex have been widely used as waterborne coating polymers for many industrial applications. A large number of open literatures have reported on the preparation and modification of acrylate latex or vinyl acetate-tert-vinyl carbonate latex, which are synthesized with semi-continuous seeded or soap-free emulsion polymerization or other advanced emulsion polymerization technology. However, the fluorine modified BA/MMA/VAc/VeoVa10 quaternary cross-linked polymer latex has not been reported in the open literatures. In this study, butyl acrylate (BA), methyl methacrylate (MMA), vinyl acetate (VAc), tertiary vinyl carbonate (VeoVa10) are the main monomers, and sulfosuccinateethoxyether alkyl monoester disodium salt(X-40) and alkylphenolpolyoxyethylene ether (LB-407) are used as the emulsifiers. Hydroxypropylmethacrylate (HPMA) and hexafluorobutyl methacrylate (HFMA) are used as the modified monomers. Potassium persulfate (KPS) is the initiator. The fluorine modified polymer latex is prepared via the semi-continuous seeded emulsion polymerization. The structure of the latex film is characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). Latex films are tested by the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and contact angle (CA). The particle size of the latex is measured with the Zetatrac dynamic light scattering instrument. The conditions for preparing the resultant latex is optimized and obtained as follows: the amount of emulsifier is 7wt%; the amount of initiator is 0.8wt%; the amount of HFMA is 5wt%. The appearance of the resultant latex is translucent and blue and the average particle size of the polymer latex and its distribution are small, which is 57.89nm and 0.048, respectively. The water contact angle increased to 95.45°.Thermal decomposition temperature of the film of the fluorine modified polymer latex is 17.33°C higher than that of the film of conventional polymer latex.
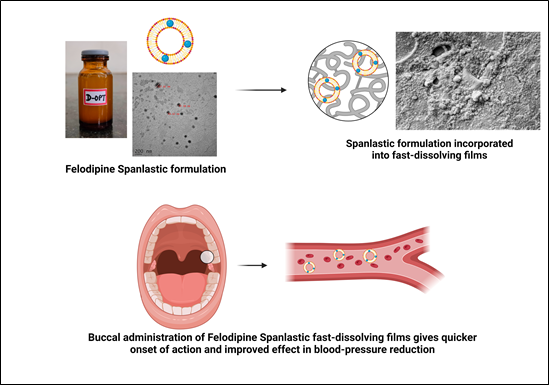
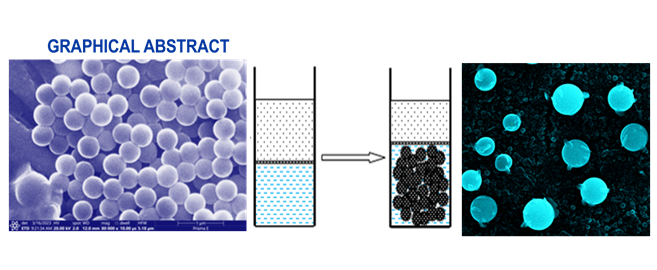
NOVEL NANO FELODIPINE-LOADED SPANLASTIC CARRIERS FOR BUCCAL DELIVERY: FORMULATION, OPTIMIZATION AND CHARACTERIZATION
Deeplaxmi Dasharath Kambli, Cleona Elizabeth Mary DCruz, Lalit Kumar, Rupesh Kalidas Shirodkar
340 просмотров
Аннотация:
Felodipine, a Dihydropyridine calcium channel …
Felodipine, a Dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonist, is widely used to treat hypertension and angina pectoris. Its highly lipophilic nature and low aqueous solubility classify it as a Biopharmaceutics Classification System Class II Drug. When administered orally, Felodipine undergoes extensive first-pass hepatic metabolism, resulting in low oral bioavailability (15%) and posing challenges for effective antihypertensive therapy. This study aimed to formulate drug-loaded nanovesicular Spanlastics within oral fast-dissolving films, enabling buccal mucosa delivery to bypass hepatic metabolism and enhance drug bioavailability. Felodipine nanovesicular Spanlastics were formulated using a modified Ethanol Injection method. Design Expert® Software Version 13 and a 2³ factorial design model determined the effect of formulation variables on response variables. The Spanlastics, characterized for particle size (ranging from 155.7 nm to 308.9 nm) and entrapment efficiencies (84.68% to 88.36%), showed lamellar, circularly shaped vesicles as observed through Optical and Transmission Electron Microscopy. These optimized Spanlastics were incorporated into oral fast-dissolving films, which exhibited substantial flexibility, sufficient mechanical strength, a disintegration time of 35 seconds, and rapid drug release of 95.99% within 5 minutes. Scanning Electron Microscopy imaging confirmed a smooth, porous, and uniform surface of the films. Short-term stability studies indicated that the films maintained stable physical and structural attributes. This research confirmed that Felodipine Spanlastic vesicles, due to their nanosize, enhance mucosal permeation and act as effective nanocarriers. Their incorporation into fast-dissolving oral films improves bioavailability through oro-mucosal tissue absorption for buccal delivery.
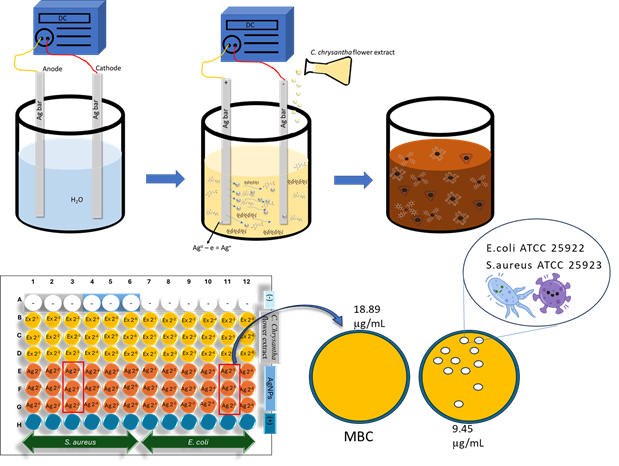
Electrochemical Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Camellia chrysantha Flower Extract: Characteristics and Antibacterial Activity
H. T. Nguyen, L. M. Hoang, H. T. Nguyen, P. H. Nguyen, T. T. V. Hoa, T. T. T. Nhung, T. Q. Huy, D. C. To
373 просмотров
Аннотация:
Plant extracts are powerful agents …
Plant extracts are powerful agents in the green synthesis of metal or metal oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications, as they are environmentally friendly and contain no toxic chemicals. This study used the electrochemical method with the Camellia chrysantha flower extract to synthesize green silver nanoparticles (AgNPs). The extract served as an electrolyte, reducing agent, and stabilizer. Without chemicals, the synthesized nanoparticles were characterized by ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and zeta potential methods. The antibacterial activity of AgNPs against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus was evaluated using minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) methods. The results indicate successful synthesis of AgNPs with a size distribution of 4-14 nm, an average size of 8.20 nm, and spherical morphology. The AgNPs synthesized by the electrochemical method using C. chrysantha flower extract exhibited a zeta potential of -29.7 mV, indicating good dispersion, and demonstrated high antibacterial activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains. Given the traditional use of C. chrysantha flowers in food and cosmetics, the synthesis of AgNPs from this extract offers potential applications in various fields including cosmetics, food, and medicine.