ТЕРМОРЕГУЛИРУЕМАЯ СМАЧИВАЮЩАЯ СПОСОБНОСТЬ ТОКОПРОВОДЯЩИХ ПЛЕНОК НА ОСНОВЕ ЭЛЕКТРОФОРЕТИЧЕСКИХ КОНЦЕНТРАТОВ НАНОЧАСТИЦ СЕРЕБРА
С. И. Бабашова, В. В. Бочаров, В. С. Суляева, Е. А. Максимовский, А. Н. Колодин, А. И. Булавченко
Полный текст (PDF), 741 просмотров
Аннотация:
Из концентрированных органозолей наночастиц серебра, …
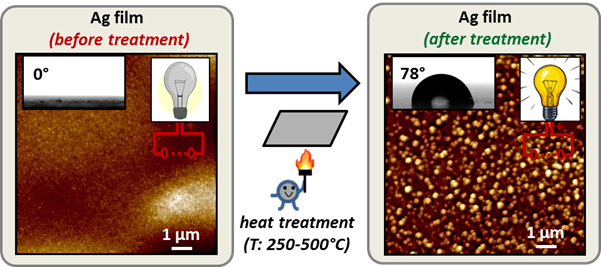
Из концентрированных органозолей наночастиц серебра, стабилизированных бис-(2-этилгексил)сульфосукцинатом натрия, методом «Doctor Blade» получены однородные, шероховатые пленки с содержанием драгоценного металла до 73 ат.%. В работе приведена подробная детализация изменений смачиваемости пленок в зависимости от условий их термической обработки в диапазоне от 50 до 500°С. Температурная зависимость углов смачивания не монотонна и предусматривает переход от супергидрофильных к слабо гидрофильным системам вследствие процессов спекания наночастиц и термического разложения стабилизатора. Экспериментально установлено, что переход от непроводящих к токопроводящим покрытиям (от 500 до 105 мОм/□) сопровождается резким ростом угла смачивания (от 25 до 78°).
Аннотация:
На основе уравнения Пуассона – …
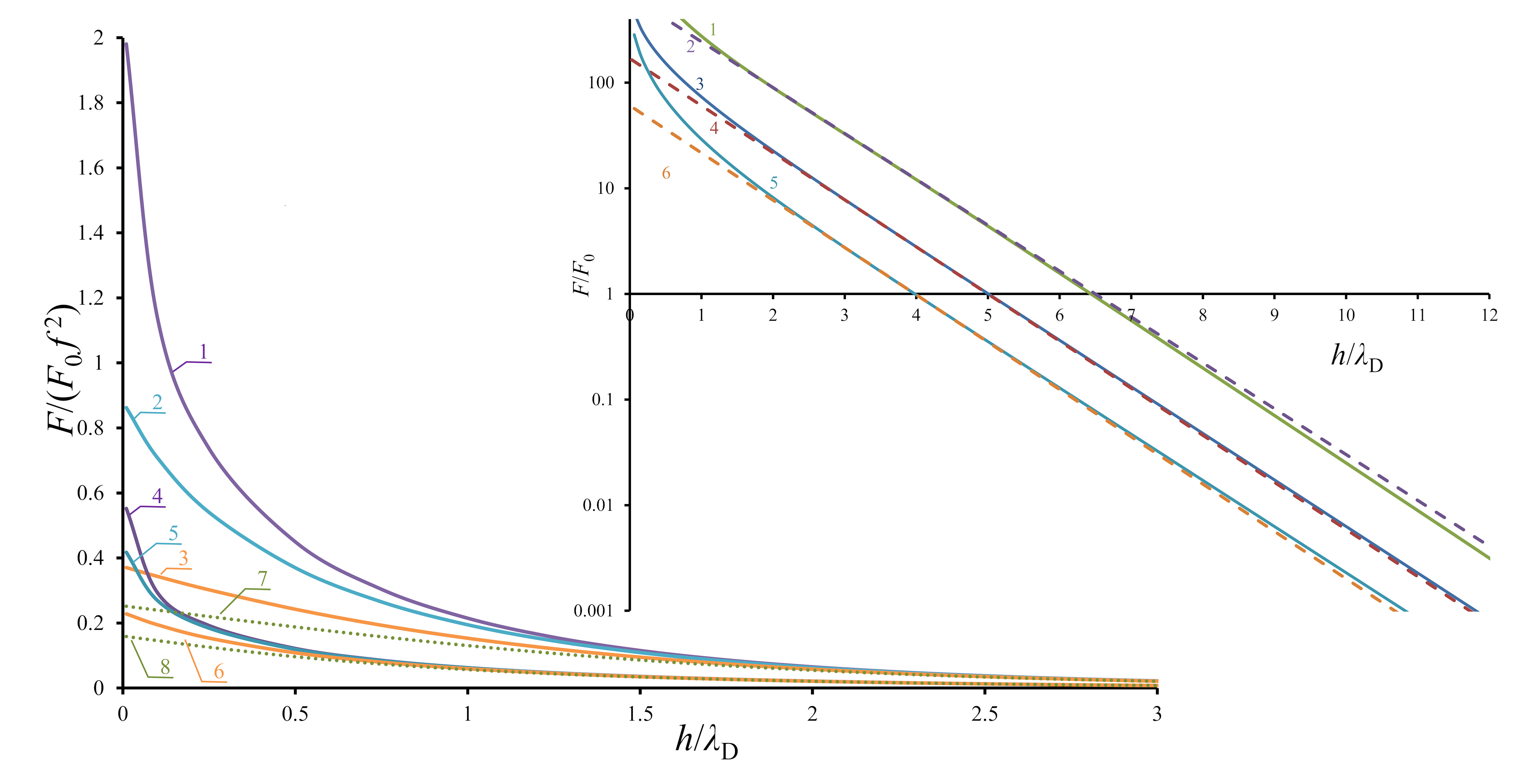
На основе уравнения Пуассона – Больцмана рассматривается электростатическое взаимодействие двух одинаковых заряженных диэлектрических сферических частиц в растворе симметричного электролита, радиусы которых значительно превышают радиус Дебая. Особое внимание уделяется случаю высоких потенциалов на их поверхностях. С использованием метода конечных элементов проводятся расчеты сил взаимодействия между частицами при условии однородного распределения заряда на их поверхностях и отсутствии внешнего электрического поля. Показано, что учет нелинейности уравнения Пуассона-Больцмана может быть необходим, даже если поверхностные потенциалы частиц достаточно малы и по формальным критериям можно использовать линеаризованное уравнение Пуассона-Больцмана. Полученные результаты могут быть полезны для понимания процессов в коллоидных системах и анализа экспериментов по взаимодействию частиц микронных размеров в растворе электролита.
СОРБЦИЯ КРАСИТЕЛЯ НЕЙТРАЛЬНОГО КРАСНОГО ЭНТЕРОСОРБЕНТОМ ПОЛИСОРБОМ МП ИЗ МИКРОЭМУЛЬСИИ АОТ В Н-ДЕКАНЕ
М. Г. Демидова, Т. Ю. Подлипская, Н. О. Шапаренко, М. К. Баракина, В. В. Татарчук, А. И. Булавченко
Полный текст (PDF), 1010 просмотров
Аннотация:
Проведена сорбция катионного красителя нейтрального …
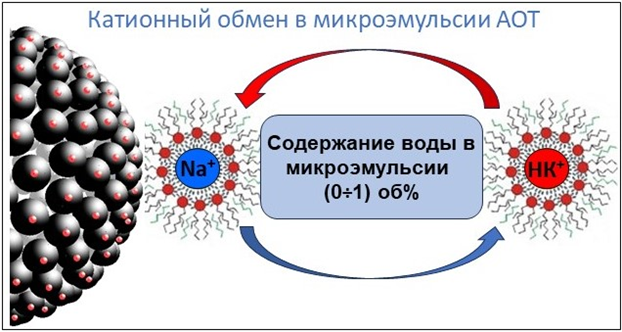
Проведена сорбция катионного красителя нейтрального красного Полисорбом МП из микроэмульсии 0.25 моль/л АОТ в н-декане при различных содержаниях водной псевдофазы. Предельная сорбционная емкость сорбента в микроэмульсии на порядок превысила соответствующую в водной фазе и составила 55 мг/г. Продемонстрированы резкое падение степени извлечения при увеличении содержания воды в микроэмульсии от 1 до 9 объемных процентов и обратимость сорбционных процессов. Анионные красители в тех же системах Полисорбом не извлекались. С ростом содержания воды дзета-потенциал частиц SiO2 уменьшался с 18 до 1 мВ. На основании полученных зависимостей предложен катионообменный механизм микроэмульсионной сорбции, включающий обмен катионов натрия и нейтрального красного между мицеллами, адсорбированными на поверхности частиц, и мицеллами в объеме микроэмульсии.
О РАСЧЕТЕ ЭЛЕКТРОКИНЕТИЧЕСКОГО ПОТЕНЦИАЛА ЧАСТИЦ В ДИСПЕРСИЯХ ДЕТОНАЦИОННОГО НАНОАЛМАЗА
Л. Э. Ермакова, Н. С. Чуйков, А. В. Волкова
Полный текст (PDF), 1077 просмотров
Аннотация:
Проведена оценка применимости различных приближений …
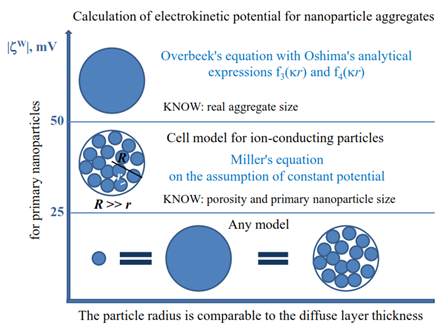
Проведена оценка применимости различных приближений теории электрофореза для расчета электрокинетического потенциала в реальных нанодисперсных системах на примере полидисперсного водного золя термоокисленного детонационного наноалмаза, содержащего агрегаты наночастиц, в зависимости от концентрации и рН растворов фонового электролита (NaCl). Установлено, что при малых величинах потенциалов |zW| < 25 мВ, найденных для первичных частиц в рамках модели Вирсемы, учет агрегирования частиц и пористости агрегатов практически не сказывается на величине электрокинетического потенциала. В интервале значений |zW| 25 - 50 мВ наиболее достоверные величины электрокинетических потенциалов агрегатов, по-видимому, могут быть получены с использованием уравнения Миллера для ионопроводящих частиц с учетом их реальных пористостей при условии постоянства потенциала. При |zW| > 50 мВ, зная реальные размеры агрегатов, в предположении их монолитности для расчета электрокинетических потенциалов можно использовать уравнение Овербека с найденными Ошимой аналитическими выражениями входящих в него функций f3(κr) и f4(κr).
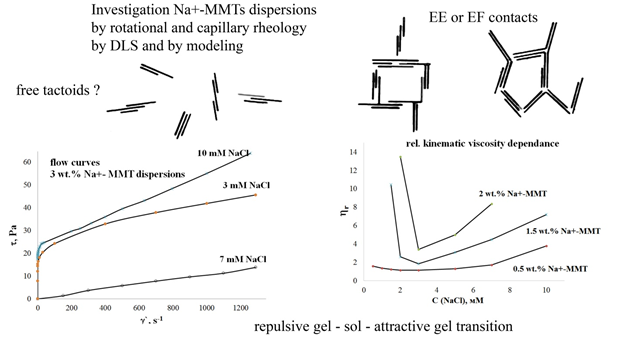
ИССЛЕДОВАНИЕ МЕХАНИЗМОВ СТРУКТУРООБРАЗОВАНИЯ В ВОДНЫХ ДИСПЕРСИЯХ NA+-СМЕКТИТОВ
Б. В. Покидько, О. А. Дулина
Полный текст (PDF), 347 просмотров
Аннотация:
В работе представлены результаты экспериментального …
В работе представлены результаты экспериментального исследования коллоидной структуры и реологии разбавленных водных дисперсий и гелей Na+-монтмориллонита, полученные методами капиллярной и ротационной вискозиметрии. С ростом концентрации индифферентного электролита водные дисперсии глинистых частиц претерпевают значительные структурные изменения, что существенным образом отражается на характере течения таких систем. При этом в узком диапазоне концентраций электролита (~3 мМ), существенно более низких по сравнению с известными из литературы значениями порогов коагуляции, фиксируется критическая концентрация, инвариантная по отношению к концентрации дисперсий в диапазоне 0.25-3.0% масс.. Наличие существенных изменений реологического поведения в данной области концентраций электролита может отражать как процессы формирования/разрушения агрегатов, так и происходящее в системе изменение механизма агрегации/структурообразования. Экспериментальные данные по реологии дисперсий были сопоставлены с теоретическими расчетами и результатами дисперсионного анализа (метод ДСР) водных дисперсий, что позволяет расширить представления о процессе структурообразования в глинистых дисперсиях.
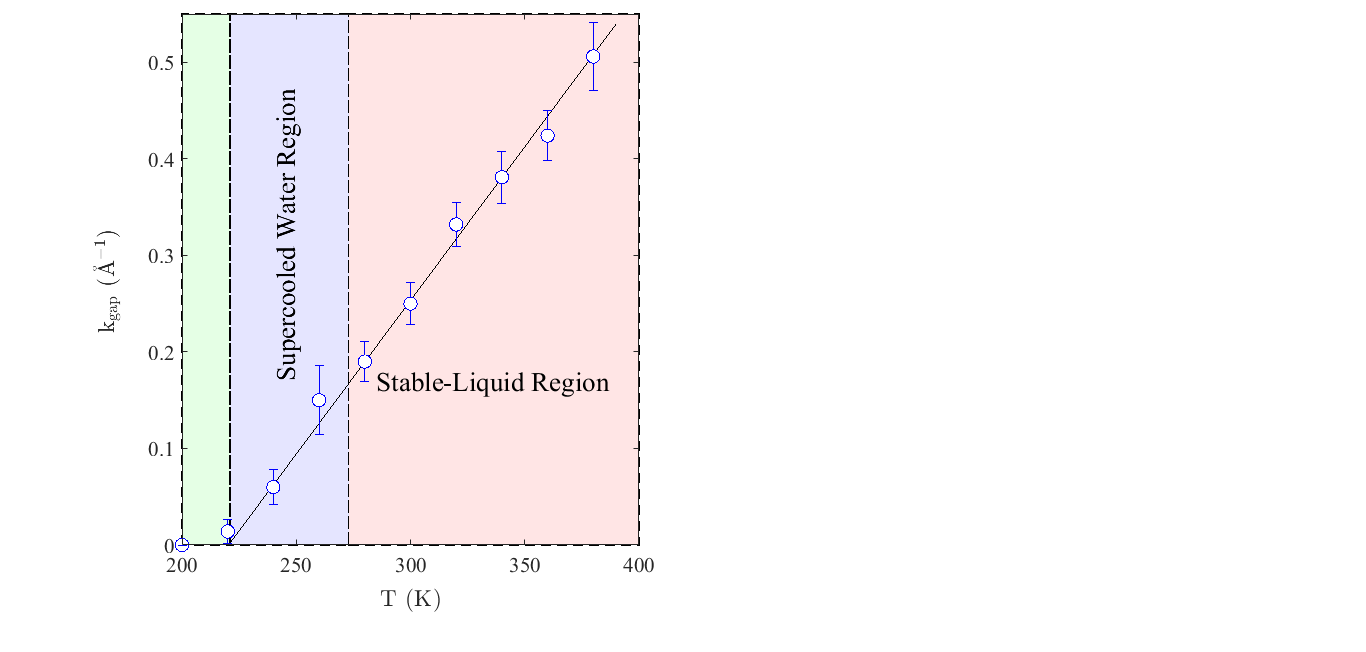
Аннотация:
Представлены результаты исследования микроскопических коллективных …
Представлены результаты исследования микроскопических коллективных возбуждений в аморфном льде низкой плотности, полученные с помощью моделирования молекулярной динамики на основе моноатомной ML-mW модели потенциала межмолекулярного взаимодействия. Рассчитанные спектры продольного и поперечного потоков обнаруживают наличие распространяющихся коллективных возбуждений продольной и поперечной поляризаций в аморфном льде для широкой области значений волновых чисел. Установлена область замешивания продольных и поперечных коллективных мод в аморфном льде низкой плотности. Показано, что температурная зависимость ширины щели kgap в законе дисперсии поперечных акустикоподобных мод описывается линейной зависимостью.
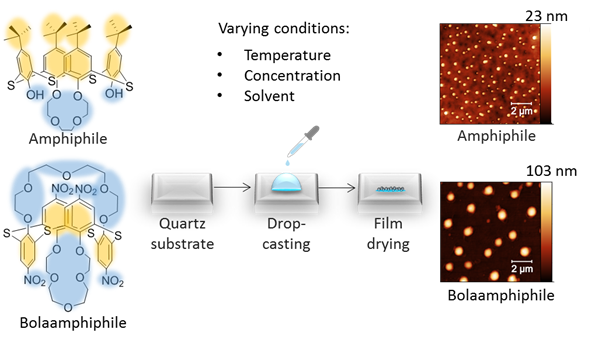
КОНТРОЛЬ САМООРГАНИЗАЦИИ ТИАКАЛИКС[4]КРАУН-ЭФИРОВ В ФОРМАХ КОНУС И 1,3-АЛЬТЕРНАТ В НАНОПЛЕНКАХ НА КВАРЦЕВОЙ ПОДЛОЖКЕ
И. Д. Четинел А. А. Ботнарь, А. С. Новиков, Е. А. Муравьева, А. Т. Ш. Иредди, П. С. Зун, С. Е. Соловьева, И. С. Антипин, Е. В. Скорб, А. А. Муравьев
Полный текст (PDF), 467 просмотров
Аннотация:
Выполнен анализ морфологических характеристик нанослоев …
Выполнен анализ морфологических характеристик нанослоев амфифильного трет-бутилтиакаликс[4]краун-4-эфира в стереоизомерной форме конус 1 и болаамфифильного нитротиакаликс[4]бискраун-5-эфира в форме 1,3-альтернат 2, нанесенных на кварцевую подложку в условиях варьирования растворителя, температуры и концентрации соединений. Квантово-химические расчеты рассматриваемых тиакаликс[4]краун-эфиров установили предпочтительную мицеллярную агрегацию (фактор упаковки p < 0.3). При визуализации нанослоев каликсаренов, полученных испарением растворителя на подложке, методом АСМ детектировались сферические ассоциаты размером 200–800 нм для соединения 1, которые укрупнялись при снижении концентрации соединения и повышении полярности растворителя и внешней температуры. В то же время дисперсность размеров ассоциатов повышалась при снижении температуры, но менялась более сложным образом в зависимости от растворителя и концентрации. Наиболее однородное распределение сферических частиц по размерам достигнуто при формировании монослоев Ленгмюра на границе раздела фаз вода–воздух при нанесении раствора соединения 1 в 10–5 M растворе в хлороформе на водную субфазу и их вертикальном переносе на подложку. В случае болаамифифила 2 сферические ассоциаты формируются при t = 23°C в 10–5 М растворе в толуоле и при 4°С в 10–4 М растворе в хлороформе, тогда как в остальных комбинациях условий нанопленка представлена нитевидными структурами (при 23°С) и тактоидными агрегатами (при 4°С). Исследование растворов амфифила 1 в хлороформе методом динамического светорассеяния позволило детектировать сферические агрегаты (диаметр частиц 202±92 нм), что указывает на ведущую роль растворителя в образовании сферических агрегатов в нанослоях, тогда как в остальных условиях на супрамолекулярную организацию каликсаренов, вероятно, существенно влияет взаимодействие с подложкой.
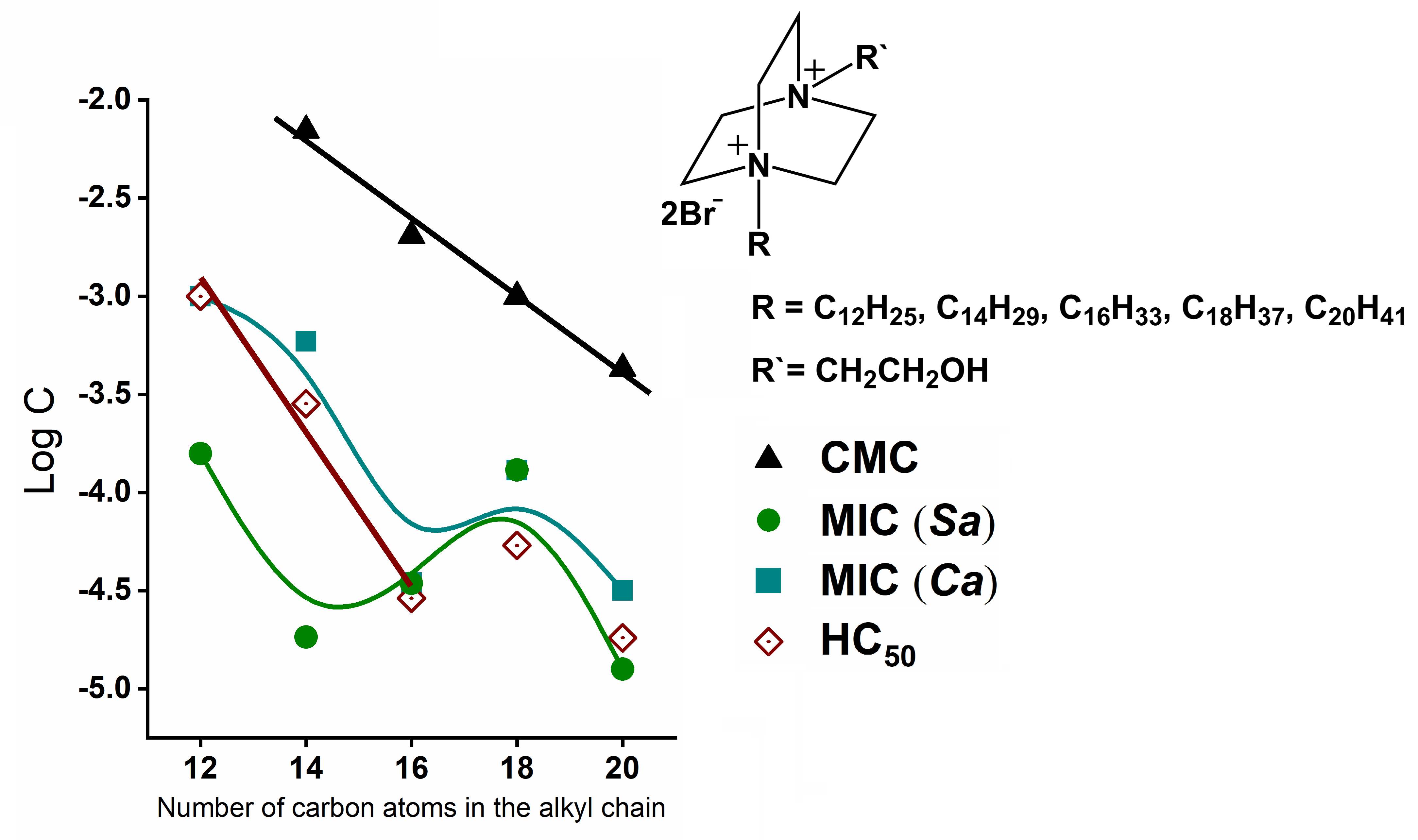
МИЦЕЛЛООБРАЗУЮЩИЕ И АНТИМИКРОБНЫЕ СВОЙСТВА СЕРИИ БИС-КВАТЕРНИЗОВАННЫХ АММОНИЕВЫХ СОЕДИНЕНИЙ НА ОСНОВЕ ПРОИЗВОДНЫХ ДАБКО
З. М. Шайхутдинова, А. С. Сапунова, Д. В. Салахиева, Т. Н. Паширова, А. Д. Волошина, А. В. Богданов
Полный текст (PDF), 271 просмотров
Аннотация:
Комплексом методов (тензиометрия, кондуктометрия, динамическое …
Комплексом методов (тензиометрия, кондуктометрия, динамическое рассеяние света, спектроскопия, флуориметрия) исследована самоорганизация длинноцепочечных бис-кватернизованных производных 1,4-диазабицикло[2.2.2]октана, содержащих гидроксиэтильную группу. Определены значения критической концентрации мицеллообразования, адсорбционные характеристики на поверхности раздела фаз воздух-вода, солюбилизационная емкость в отношении плохорастворимого в воде красителя ОранжОТ, числа агрегации и размеры ассоциатов. Установлено влияние структуры исследуемых соединений (длина алкильной цепи и заряд головной группы) на мицеллобразующие, антимикробные свойства и гемолитическую активность.

Slow Freezing and Thawing Dynamics of Human Ejaculate on Extremely Water-Repellent Carbon Soot Coatings – Implications to Sperm Cryopreservation
Karekin D. Esmeryan, Miglena M. Paneva, Petar P. Panev, Todor A. Chaushev
508 просмотров
Аннотация:
Paradoxically, but the humans cannot …
Paradoxically, but the humans cannot survive at ultralow temperatures, while individual cells, such as the spermatozoa, can be stored at cryogenic conditions. This facilitates the in-vitro fertilization in cases of male infertility, but the success of assisted reproduction is not guaranteed due to cryodamage of part of the gametes. Recent innovations in carbon nanotechnologies provide perspectives to resolve the existing problems in reproductive medicine, since the flame deposition of rapeseed oil soot on the surfaces of freezing tools favors the cryopreservation of human semen. The water-repellent soot supports heat exchange rates allowing timely osmotic removal of the intracellular water and retained chemical equilibrium in the cells. It is unknown, however, whether the non-wettability of soot is responsible for the enhanced cryopreservation or the dynamics of sperm freezing and thawing influences the outcome. To understand this, 50 µL semen without and with 50 vol. % cryoprotectant SpermFreezeTM are frozen within twenty minutes on two types of soot coatings by simultaneously cooling all components of the cryogenic chamber, leading to ice-liquid content in the droplets that eliminates the singular tip, followed by uniform melting via thermocapillary convection. The pre-cooling of soot-coated substrates and the absence of cryoprotectant generates an abrupt upward-moving freezing front and increases the total ice mass in the semen, creating a cone tip – processes, presumably worsening the cells’ viability. These novel results reveal that the fraction of ice crystals and their spatial distribution could be adjusted by selecting appropriate carbon nanostructures and cooling regimes, targeting future harmless sperm freezing.
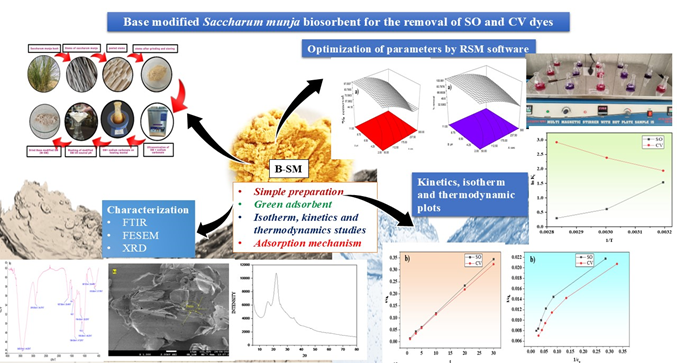
Statistical Optimization and Evaluation of the Adsorptive Efficiency of Base Modified Saccharum Munja Biomass for Safranine O And Crystal Violet Dyes in Single and Binary Systems
Anisha Grewal, Aniket Singh, Nishita Sharma, Partiksha Panghal, Sonika Singh, Surender Kumar
531 просмотров
Аннотация:
In this study, we have …
In this study, we have utilized the base treated Saccharum munja for the removal of Safranine O (SO) and Crystal Violet (CV) dyes from water. The as-synthesized composite was characterized by using various techniques to study the morphological and functional features. Response surface methodology was used to optimize the effect of various parameters sch as pH, dosage, and concentration on the adsorption process. Moreover, the kinetics and isotherm of the adsorption process were evaluated using various models. The best-fitted kinetic model was the Pseudo-Second-Order model for both the dyes. The Freundlich isotherm model was found to be the most appropriate for SO and CV dyes suggesting the multilayer adsorption. Further, the adsorption process was favorable as the value of 1/n falls between 0-1. The Langmuir maximum adsorption capacity (qmax) for SO and CV dyes was found to be 121.80 mg/g and 143.67 mg/g respectively. The regeneration study was performed to check out the reusable capability of the composite and it showed a good regeneration stability upto five adsorption-desorption cycles. In conclusion, Saccharum munja can effectively reduce environmental pollution and offer a sustainable solution for dye removal.
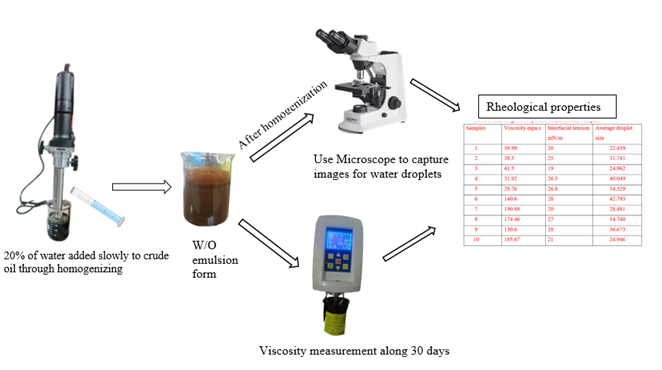
Influence of Continuous Phase Properties and Homogenization Conditions on Water Droplet Size Distribution in Water/Crude Oil Emulsions
Fatima A. Jassim, Sarmad T. Najim
235 просмотров
Аннотация:
This study investigates the impact …
This study investigates the impact of homogenization parameters and the properties of the continuous phase of crude oils on the droplet size distribution, stability, and viscosity of emulsions composing it. Understanding these relationships is essential for enhancing the preparation and processing of several emulsion-based products, such as food, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical items. To achieve results, the study employed a measured experimental design to examine the effects of homogenization at speed (3000-12000 rpm) in (3-9 minutes) on emulsions prepared of various continuous phases of crude oil. The droplet size distribution and viscosity of the crude oil emulsions were carefully measured and analyzed.
Key findings demonstrate that increasing homogenization speed and time resulted in smaller droplet sizes and an increase in emulsion stability. Moreover, the continuous phase viscosity of crude oil affects both the droplet size and the viscosity of crude oil emulsion causing the larger droplets and higher emulsion viscosities due to an increase in continuous phase viscosity. Additionally, the study shows that the emulsion viscosity continuously increases over time (aging), indicating that it is suitable for long-term stability. The novelty of this work lies in its comprehensive exploration of the interconnected effects of homogenization parameters and continuous phase properties on emulsion characteristics. By providing insights into these relationships, the study contributes to a deeper understanding of emulsion behavior and offers valuable guidance for the development and optimization of emulsion-based products.
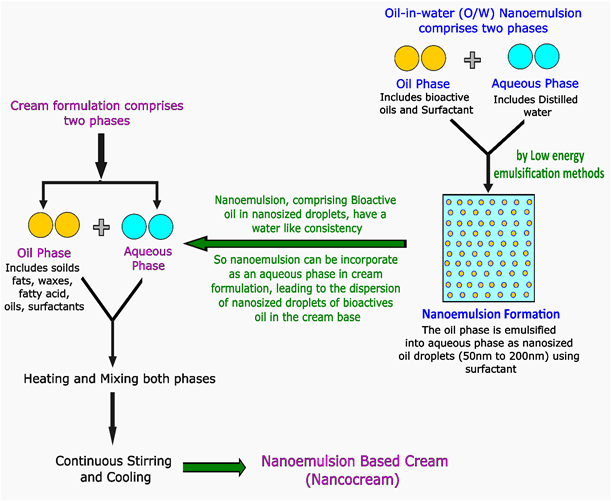
Formulation and Evaluation of Nanoemulsion-Based Cream using Green Ingredients Exhibiting Enhanced Performance Characteristics
Daphne Nguyen, Manish Kumar
558 просмотров
Аннотация:
The present study focuses on …
The present study focuses on the formulation and evaluation of a nanoemulsion-based cream (nanocream) using green ingredients, aimed at enhancing performance, stability, and sustainability. The nanoemulsion was developed through the low-energy phase inversion temperature (PIT) method, which successfully protected green bioactive compounds like vitamin E, cinnamon oil, jojoba oil, and peppermint oil from degradation. A series of nanoemulsions were prepared using varying ratios of oils and surfactants and evaluated for stability, transparency, and droplet size. The optimized nanoemulsion, with a mean droplet size of 121.3±1.1 nm and a low polydispersity index (PDI) of 0.094±0.001, demonstrated high uniformity and stability. This optimized nanoemulsion was further used as the cream’s aqueous phase, forming a nanocream that exhibits enhanced permeation of nanoscale bioactives through a membrane and improved overall performance characteristics. In vitro membrane permeation studies revealed that the optimized nanocream achieved a permeation rate of 97.1%, substantially outperforming the control cream. In vitro antimicrobial studies showed comparable efficacy to standard market preparations containing synthetic agents. The nanocream also demonstrated long-term stability over six months, maintaining structural integrity without phase separation or significant changes in pH and spreadability. The nanoemulsion-based cream formulated with eco-friendly ingredients hence offers enhanced skin permeation, superior bioactive delivery, and stable performance, making it a promising candidate for topical skincare and antimicrobial applications.
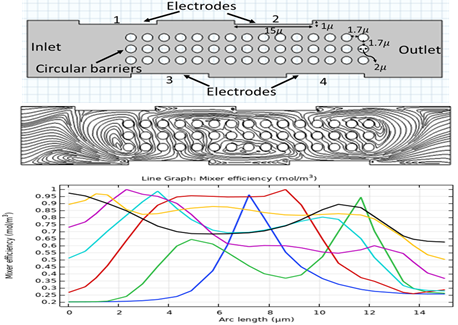
Аннотация:
Micromixers represent microchannel devices that …
Micromixers represent microchannel devices that promote effective fluid integration within a constrained spatial domain and a specified flow pathway. The mechanism of induced-charge electroosmosis has garnered substantial attention from the microfluidics scholarly community over the past decade. In this study, an electroosmotically actuated micromixer amalgamates two disparate fluids that enter through individual inlets into a unified channel measuring 15 μm in width and 80 μm in length, respectively. A sinusoidal electric potential, with a peak value of 0.1 V at a frequency of 8 hertz, is applied across the electrodes. To enhance the operational efficacy of the micromixer, 45 uniform circular barriers are integrated within the microchannel. According to the simulation outcomes, the micromixer attains an exemplary mixing efficiency nearing 0.97 and exhibits promising potential applications across a diverse array of fields, including biochemistry and biomedical sciences.